Deckplate
Initial Analysis and Measurements:
- Measured the existing deck plate from a previous design (36″ x 24″ x 1/8″ thick).
- Added 1″ x 1″ square cutouts at each corner to align with the chassis.
- Included 1/4″ slot screw clearances on all four sides to maintain deck plate integrity.
Design Iteration:
- Developed the first design version in SolidWorks to analyze and plan adjustments based on measurements.
Material Selection:
- Defined requirements for the deck plate material, including resilience to vibrations, G-forces, weight capacity (35 lbs), speed (0-5 mph), and minimal deflection (< 1/4″).
- Selected aluminum 5052-H32 for its lightweight, strength-to-weight ratio, impact resistance, and heat dissipation properties, ideal for maintaining stability, safety, and electronic component protection.
Testing for Durability:
- Conducted load testing by placing a 20-lb cinder block on the deck plate to assess weight support and rear down-force, enhancing rear traction via Finite Element Analysis.
- Strategically positioned the electronics suite at the front of the vehicle for optimal balance and intelligent function.
First Product
Final Product
Redesign and Modifications:
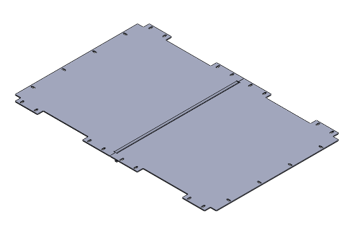
- Split the deck plate into two symmetrical pieces with a 90-degree bend to increase stiffness and load support.
- Added cut-outs on each side to allow mounting brackets to sit flush with the chassis, enhancing modularity and ease of service.