Cybersecurity is typically conceived as a technical topic. In reality, the topic is multidisciplinary, and some aspects of the topic are best understood through a social science lens. This course addresses the social, political, legal, criminological, and economic dimensions of cybersecurity through a social science framework. Students are introduced to a human-factors approach to understanding cybersecurity threats. Attention is given to the social factors that contribute to cyber incidents and the political and legal mechanisms that are developed to control the behaviors of those who create risks cybersecurity incidents. The class also explores how cybersecurity is studied by social scientists in psychology, political science, criminology, economics, sociology, international studies, and other social science disciplines.
- Compare how basic psychological, sociological, criminological, political, economic, and legal theories and models explain cybersecurity.
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of those theories in understanding the connections between human behaviors and cybersecurity.
- Define key concepts including cybersecurity, cybercrime, cyber criminology, cyber law, digital forensics, human factors, cyber policy, cyber risk, cyber threats, and cyberwar.
- Identify how professionals in various cybersecurity careers apply these multidisciplinary concepts in their daily routines.
- Describe how hypotheses and research questions are formed in studies addressing cybersecurity through a social science lens.
- Describe how data are collected, measured, and analyzed in studies addressing cybersecurity through a social science lens.
- Identify how marginalized groups have confronted challenges and concerns related to cybersecurity as well as how these groups have contributed to our understanding about the topic.
- Explain how the application of social science theories, principles, and research strategies have contributed to our understanding of cybersecurity at the societal level.
Course Material
Bhattacherjee, A. (2012). Social science research: Principles, methods, practices Links to an external site. Links to an external site.
Class Discussions
Discussion 1: Describe the top three careers of cyber social science fields that you would be interested in considering. What is it about those jobs that you find interesting?
Initial Post
Three career fields that interest me the most within the cyber social science concentration are penetration testing, governance compliance & risk management, and network security management. The thing I find most interesting about being a penetration tester is the social engineering aspect of it. Working in government compliance is interesting because it involves looking at culture and determining what laws are going to protect the most people and why. Network security management is interesting because it involves managing a group of people to interact digitally without causing vulnerabilities.
Response
I too selected penetration testing as a field that I am interested in. I agree figuring out how people work and what makes them vulnerable is very fascinating. When I hear things like ‘password’ and ‘123456’ are some of the most common passwords it makes me wonder how vulnerable are our systems. There is a lot of work out there to help teach people how to protect themselves digitally.
Discussion 2: What do you think about the principle of determinism as it relates to computer hacking?
Initial Post
Determinism is defined in our reading material this week as a behavior that is caused, determined, or influenced by preceding events. Determinism relating to computer hacking could make it difficult to understand all of the causes and influences since relating scientific principles to sociological concepts can be difficult and there isn’t solid evidence detailing the cause and effect of all social interactions. Since computers are completely created, utilized by, and changed by people it is challenging to associate the deterministic principles that lead to unauthorized access to computer systems. We could hypothesize that some of the preceding causes lead people to unauthorized access to computer systems based on the studies of sociology and psychology. Some motivating factors that could lead people to hack are personal ego, financial gain, political power, revenge, social status, etc… To better understand what determining factors lead to crimes like computer hacking, the context of what is being hacked, who is hacking, and what could be gained from this infiltration would need to be examined in detail.
Response
I agree that the availability of ‘opportunity’ in human-built computer systems is a deterministic cause of hacking. People have an intrinsic need to understand and know the complete framework of how our systems are built, run, and could be compromised. This need for discovery coupled with other influencing factors such as financial gain or notoriety could lead individuals or groups to criminally infiltrate systems that they have no ownership in.
Discussion 3: “Apply the phrase victim precipitation to cyber victimization”
Initial Post
Applying the theory of victim participation to cyber victimization is when a victim’s digital actions lead to their cyber victimization. Victim participation starts with the individual posting about themselves online and making their digital profiles, information, and positions available publicly. Cyber attackers targeting individuals use the information they find online to launch an attack and/or elicit a response. Examples of cyber victimization are harassment, cyberstalking, sexual exploitation, bullying, etc… A few ways to prevent victim participation is being careful about the information shared online and what applications it is shared on. Some online platforms have better security and moderation helping prevent victimization. Also, not all information should be shared digitally because it may attract attackers to cause harm.
Response 1
******* great example of victim participation in cyber victimization. I am sorry that the situation happened to you. There are many instances where attackers take things out of context and attempt to harm someone based on their perceived understanding of a concept, a person, or an argument. The more information made available online opens people up to victimization in unrealized ways. Using large online public forums such as Reddit, Discord, Facebook, etc… are places where cyber victimization happens a lot.
Response 2
I liked how you cited weak security measures as a form of victim participation. Not protecting oneself with new strong passwords, good digital hygiene, and not using or updating antivirus software are all ways that potential hackers may try to victimize someone and steal or alter their information. If people are going to use information technology it is their responsibility to understand the systems they are using and the ways they could be victimized so they can take measures to fortify themselves digitally.
Discussion 4: “Identify which theories you think best explain cybercrime and discuss what you like about that theory.”
Initial Post
The theory of Neutralization best describes cybercrime because it looks at how people process information and rationalize their actions. Most people understand the basics of right and wrong and know if their actions are observed by others how it would or could be received. I liked this theory the most because it looks at why people justify wrong behavior as okay. People often make excuses to themselves as to why its okay for doing something wrong or doing harm to others. Looking at how people justify crime is a great place to start in finding ways to prevent it. If people are educated in the harms caused by crime they may be more likely to not participate if they can’t justify it.
Response 1
I liked how you compared the severity of a crime to how strong the justification is. People understand the basics of cause and effect and can process the potential outcomes of questionable acts. If cybercriminals didn’t see any repercussions from a small level of intrusion they may try and escalate their actions to a higher level of intrusion under a higher level of justification. For instance if a person hacks into a system to see if they can, they may tell themselves nobody got hurt or they should have had stronger security or I wouldn’t be able to do this. The next time they attempt to break into a system they may try something harder or more destructive for more of a challenge and have a stronger justification because of the successful outcome of the first intrusion. Their justification would be stronger because of their previous success and the added challenge would add to that.
Response 2
I think your description of RST hits on an insightful point that can help us understand one of the reasons people engage in cybercrime. Individuals who seek that reward interest in receiving a high from successful intrusion could be compared to how drug addicts seek a rewarding feeling from the substances they ingest. If the first intrusion activity creates an elevated level of satisfaction and accomplishment the perpetrator may try the activity again with higher stakes for a similar or more increased feeling of reward. This can be similar for drug users, after the first initial experience they may take the substance more frequently and in larger doses seeking the reward of similar or more intensive effects.
Discussion 5: Watch this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BpdcVfq2dB8Links to an external site. and pay attention to what the biggest risk of cyber threats are. After watching the video, post an entry in the discussion board describing what you think about the “human firewall”. Respond to two other students’ entries.
Initial Post
The “human firewall” is cybersecurity’s first and final line of defense that everyone is responsible for. The speaker noted that humans are the biggest risk and the biggest line of defense when it comes to securing our information systems. What people know, do, or don’t do makes all of the difference in computer security. The assigned article this week, “Botching Human Factors in Cybersecurity in Business Organizations” noted that 95% of all cybercrime is human enabled. This means the most effective way we can prevent future cyber attacks is regular, continuous education and training on cybersecurity that everyone is required. Since cybercrime has become so frequent and ubiquitous where year after year trillions more is lost than the year before, our organizations are missing the largest threat and solution. Increased education should be the number 1 investment to protect our systems. The speaker shared that the average intelligent person needs to be told something 6 times before they remember it. This shows how repeated regular learning will produce optimal outcomes in security. A possible solution for improving security and strengthen the “human firewall” is organizations should incentivize for good cyber hygiene and penalize poor cyber hygiene. Creating an incentive versus penalty program could help inspire people to take seriously their part of the “human firewall” in securing information systems. Organizations are a team and using the metaphor by comparing it to a chain, they are only as strong as the weakest link. It only takes one person’s mistake to allow an intrusion that brings everyone’s system down.
Response 1
I agree that most people view cybersecurity as being highly advanced and overly complex. However, the majority of risks are simple and easily avoidable. Having a knowledgeable workforce that doesn’t view information security as “not my responsibility” provides the best protection for our systems from intrusion. Regular on going education is a terrific way to implement this because many attacks break through people’s common sense. The social engineering activities the speaker shared showed how easily people offer personal information that could be used against them. When it comes to information trust less, stay skeptical, and increase education.
Response 2
I disagree that it is a terrible idea that all employees should be mindful of security. If people can learn to use computer systems they should be able to learn how to use them safely. Organizations are not expecting everyone to be security experts. They are telling people if you use our systems we want you to use them safely. If people purchase firearms they are not expected to be firearm experts but they are expected to use a basic level of safety. When people log on to information systems they should be able to follow the rules completing simple tasks like protecting their passwords, choosing challenging passwords, not clinking on phishing links, or loaning out their access card. If people can’t follow basic guidelines perhaps they shouldn’t be entrusted to use the system. Most organizations can’t afford a maximum level security program that is used for classified material. Keeping a maximum security program in most computer use settings would be unrealistic in labor and equipment in many instances.
Discussion 6: Cyber threats
Watch this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BpdcVfq2dB8Links to an external site.
and pay attention to what the biggest risk of cyber threats are. After watching the video, post an entry in the discussion board describing what you think about the “human firewall”. Respond to two other students’ entries.
Initial Post
The “human firewall” is cybersecurity’s first and final line of defense that everyone is responsible for. The speaker noted that humans are the biggest risk and the biggest line of defense when it comes to securing our information systems. What people know, do, or don’t do makes all of the difference in computer security. The assigned article this week, “Botching Human Factors in Cybersecurity in Business Organizations” noted that 95% of all cybercrime is human enabled. This means the most effective way we can prevent future cyber attacks is regular, continuous education and training on cybersecurity that everyone is required. Since cybercrime has become so frequent and ubiquitous where year after year trillions more is lost than the year before, our organizations are missing the largest threat and solution. Increased education should be the number 1 investment to protect our systems. The speaker shared that the average intelligent person needs to be told something 6 times before they remember it. This shows how repeated regular learning will produce optimal outcomes in security. A possible solution for improving security and strengthen the “human firewall” is organizations should incentivize for good cyber hygiene and penalize poor cyber hygiene. Creating an incentive versus penalty program could help inspire people to take seriously their part of the “human firewall” in securing information systems. Organizations are a team and using the metaphor by comparing it to a chain, they are only as strong as the weakest link. It only takes one person’s mistake to allow an intrusion that brings everyone’s system down.
Response 1
I agree that most people view cybersecurity as being highly advanced and overly complex. However, the majority of risks are simple and easily avoidable. Having a knowledgeable workforce that doesn’t view information security as “not my responsibility” provides the best protection for our systems from intrusion. Regular on going education is a terrific way to implement this because many attacks break through people’s common sense. The social engineering activities the speaker shared showed how easily people offer personal information that could be used against them. When it comes to information trust less, stay skeptical, and increase education.
Response 2
I disagree that it is a terrible idea that all employees should be mindful of security. If people can learn to use computer systems they should be able to learn how to use them safely. Organizations are not expecting everyone to be security experts. They are telling people if you use our systems we want you to use them safely. If people purchase firearms they are not expected to be firearm experts but they are expected to use a basic level of safety. When people log on to information systems they should be able to follow the rules completing simple tasks like protecting their passwords, choosing challenging passwords, not clinking on phishing links, or loaning out their access card. If people can’t follow basic guidelines perhaps they shouldn’t be entrusted to use the system. Most organizations can’t afford a maximum level security program that is used for classified material. Keeping a maximum security program in most computer use settings would be unrealistic in labor and equipment in many instances.
Discussion 7: Watch this video Links to an external site.
about a 12-year-old cyber security expert. Pay attention to how he has embedded himself into the cybersecurity culture. Also, pay attention to how the ideas of knowledge, technology, and secrecy relate to his expertise. On the discussion board post an entry about how the video relates to something you read for this class – either from the readings or this module.
Initial Post
Rubin Paul is a white hat hacker as described in module 6. His leading personality trait is agreeableness because his main motivation for hacking is to help other people understand and respond to vulnerabilities in using IoT devices. Rubin described the vulnerabilities that people face when logging into unsecured Wi-fi networks. His explanation of why unsecured connections are unsafe is an example of the ‘human firewall’ we discussed in module 6’s discussion post. People are the first line of defense when it comes to the security of information. Without proper training and education relating to the use of cyber tools, people open themselves to unknown vulnerabilities and victim participation. Victim participation was discussed in module 4 where victim’s actions sometimes lead to their victimization. The news anchor showed victim participation when he unwittingly signed into a fake Twitter website and entered his username and password giving the attacker his login information. Luckily his mistake was made to a white hat hacker who was trying to educate people on victim participation instead of a malicious hacker whose intention would be to victimize the participant.
Response
I liked how you compared this news segment to our learning about research through surveys. I would add that this reporting team’s research would also fall into the case study definition of ‘participant as observer’ since the news anchor used his access to a personal account on an unsecured wi-fi demonstrating victim participation and showing why people should not connect to any network. Ruben was easily able to steal the anchor’s user’s identification and authentication information with a simple packet sniffing technique. The reporting team linked this unsafe behavior to simple IoT devices that could be used to spy on and victimize children. I too commented that Ruben Paul demonstrates the qualities of a white hat hacker. In his interview and his speaking events, he tries to promote public awareness and common deficiencies in cyber hygiene by discussing different ways we can all be more conscious and proactive to prevent victimization.
Discussion 8: Identify two research questions that researchers might address related to the social aspects of cybersecurity. Respond to two other students’ entries in terms of what you think about the questions they identified.
Initial Post
1. How much is cybersecurity education taught in the public school system? In which ways is it lacking and should be increased? When students are exposed to internet safety educational materials, how much does their behavior change?
2. What demographic experiences the highest amount of cyber victimization, why is that, and what efforts can be made to reduce that trend?
Response 1
Great questions!
“1. What characteristics do cyber attackers give bot accounts to make them more trustworthy in spreading misinformation to real social media users?” This question would be a valuable study to look at. A better understanding of how attackers are deceiving people will help in providing materials to educate potential cyber victims on how to protect themselves and fortify themselves against malicious or false information. Misinformation propaganda spread by bots is a growing problem that should be researched to find solutions to mitigate these threats.
” 2. How does a person’s behavior on social media influence their risk of becoming a victim of identity theft?” Studying social media victim participation regarding identity theft would be a valuable topic to understand and provide insight into. People post all sorts of revealing information about themselves on social media, sometimes information that allows attackers to gain access to their accounts. The results of studying this question could improve how cybersecurity is discussed with the public and how they are encouraged to interact in the digital space.
Response 2
I liked your questions regarding social media and security awareness and misinformation.
“1. What is the impact of social media use over multiple generations in relation to information security awareness.
2. How is misinformation present on social media platforms reviewed and perceived by every generation.”
A better understanding of generational differences in informational security awareness would provide valuable insight into how age groups interact on the internet and how they could be provided with better-tailored learning materials. The activity of each generation on social media has unique uses and interactions that could be understood better to promote awareness and tactics in preventing victim participation. Misinformation has been a growing trend on social media and understanding how different age group populations receive and adopt those viewpoints would help in its prevention. What a teenager sees online and believes is probably very different from what someone in their seventies does. Relativism in age and technology interactions could offer a lot of insight into how people are targeted and how their behaviors allow them to be deceived or attacked.
Discussion 9: What does economics have to do with cybersecurity? Respond to two other students posts.
Initial Post
Economics studies production, consumption, and the transfer of wealth. This is relevant to cybersecurity because information technology has completely transformed economics. Most financial transactions are completed digitally where funds are held on and transferred to and from electronic ledgers. This use of technology has offered opportunities for attackers to try and steal those digital funds or view potentially damaging information. The news often shares stories where cybersecurity has been subverted allowing employees to embezzle funds from an organization, locking owners out of their data for ransom, stealing and releasing private financials that erode trust, and stealing proprietary information. Cybersecurity helps prevent these destructive activities and preserves the strong functionality of the economy. Without protections, the economy would be in complete chaos without any trust in the systems we rely on.
https://search.yahoo.com/search?fr=mcafee&type=E210US105G0&p=define+economics
Response 1
I liked how you compared cybersecurity to economics. This is not a comparison that is apparent at first. However, there are a lot of similarities between both disciplines. They both have examples of goods, services, and employment. They both function with great reliance on each other’s functionality for success. It’s hard to imagine a modern world where these two branches of study aren’t completely interconnected. Modern financial systems wouldn’t function in the same ways without a secured digital infrastructure and cybersecurity wouldn’t be what it is without a financial system to provide incentives and products to achieve its goals.
Response 2
I liked how you discussed the need for organizations to protect their digital property from economic losses. There are many critical concepts discussed in Cybersecurity educational materials that discuss this economic necessity. Policies like a Disaster Recovery Plan and a Business Continuity Plan show how interrelated and interconnected these two fields of study are. They display how an organization’s financials are reliant on security. Without security, most businesses would struggle to function due to regular losses related to breaches that could stop productivity and inhibit stability. The research you added reinforces this argument by showing how economic leadership identifies this as the most dangerous threat the global economy experiences.
Discussion 10: Why do you think individuals don’t report cybercrime victimization? Describe your views and respond to two other students posts.
Initial Post
People who experience victimization in cybercrime feel a lot of emotions including stress, anxiety, fear, embarrassment, anger, and isolation. Of these feelings, emotions of embarrassment as the leading cause of not reporting victimization. Individuals who have been tricked through online behavior may feel shame for falling for deception. This feeling of shame may cause them to not report the crime because it will bring to attention their mistake and make them feel unintelligent. This could be especially embarrassing if they were a victim of romance fraud. Falling for an attack because of loneliness may be extraordinarily rattling because the victim is more emotionally involved and cheated.
Response 1
I liked your reasoning for the lack of reporting. I shared that I felt like embarrassment was the leading reason for these crimes being underreported because they didn’t want others to know they made a mistake. Your second reason is a great point that hadn’t occurred to me. Many times people don’t realize that they have been breached. If someone’s information is hacked or if malware is secretly uploaded to their device they may not realize that they have been victimized and won’t know to report it.
Response 2
I liked your reasoning for why victims may not report being duped. If a person falls for internet fraud it may seem like more work than it’s worth to report the victimization. The process of figuring out where and how to report cybercrime could seem daunting to a person who has never reported such crimes before. If the victim didn’t lose very much in the attack they may feel it’s not worth their time to report it.
Discussion 11: Why do you think individuals don’t report cybercrime victimization? Describe your views and respond to two other students posts.
Initial Post
People who experience victimization in cybercrime feel a lot of emotions including stress, anxiety, fear, embarrassment, anger, and isolation. Of these feelings, emotions of embarrassment as the leading cause of not reporting victimization. Individuals who have been tricked through online behavior may feel shame for falling for deception. This feeling of shame may cause them to not report the crime because it will bring to attention their mistake and make them feel unintelligent. This could be especially embarrassing if they were a victim of romance fraud. Falling for an attack because of loneliness may be extraordinarily rattling because the victim is more emotionally involved and cheated.
Response 1
I liked your reasoning for the lack of reporting. I shared that I felt like embarrassment was the leading reason for these crimes being underreported because they didn’t want others to know they made a mistake. Your second reason is a great point that hadn’t occurred to me. Many times people don’t realize that they have been breached. If someone’s information is hacked or if malware is secretly uploaded to their device they may not realize that they have been victimized and won’t know to report it.
Response 2
I liked your reasoning for why victims may not report being duped. If a person falls for internet fraud it may seem like more work than it’s worth to report the victimization. The process of figuring out where and how to report cybercrime could seem daunting to a person who has never reported such crimes before. If the victim didn’t lose very much in the attack they may feel it’s not worth their time to report it.
Discussion 12:
Watch this video Links to an external site.
and explain what it has to do with routine activities theory. Respond to at least one other classmate’s posting.
Initial Post
The Routine Activity Theory explains that crime occurs when three aspects happen at the same time and place; there is a motivated offender, a suitable target, and an absence of capable guardians. According to this theory, cybercrimes are on the rise because the number of targets is accelerating due to the increase of cyber usage by potential targets, the lack of capable guardians due to the need for cybersecurity professionals, and motivated offenders are growing because of the increased availability of cyber technologies for potential criminals. This video supports this theory where several examples of this crime theory took place where the factors all align. The people who were interviewed tried to engage in online shopping and were victimized as a result. The reporting also showed numerous fake websites attempting the same activity by scamming unsuspecting online users. Furthermore, this segment included the rising lack of capable guardians by explaining how Facebook is continuing to remove fake user accounts totaling over a billion. The trend reported in this video will likely continue to rise as more people and devices connect to the internet. The need for cybersecurity professionals will continuously increase because new candidates entering this field aren’t likely to match the exponential adoption of this emerging technology. This theory is key to understanding where motivated offenders are hiding and waiting for their next victim. Understanding this allows for efforts to be made to increase where capable guardian resources can be expanded to minimize this threat.
Response 1
I liked how your post included instances where this theory could explain sudden increases in crime because of growing suitable targets. The rise in online activity during the COVID-19 pandemic and holiday shopping are great examples to study and understand where security resources are most effective. Understanding this theory could help with the optimal dispensation of scarce security personnel to where they are most effective and promote increased funding for promotional recruitment into cybersecurity professions because of the rising need.
Response 2
I liked how you offered examples of suitable victims and what made them more vulnerable to victimization. People with less experience with ICT devices and activities like elderly people are more likely to fall for scamming acts for reasons that align with this theory. New users are adopting this technology because of the benefits that it offers in increased availability, connectivity, and time savings. Attackers see these increases in vulnerable users and capitalize on them. This increase in novice users increases the need for more capable guardians compounding the urgent need for more protection. Understanding these correlations helps focus the organization’s cybersecurity resources where they are needed most.
Journal Entries
Journal Entry 1
Review the NICE Workforce Framework. Are there certain areas that you would want to focus your career on? Explain which areas would appeal the most to you and which would appeal the least.
Workforce Framework for Cybersecurity (NICE Framework)
The types of work I enjoy the most are critical thinking, problem solving, and technical writing. While these qualities could be utilized in all categories of cybersecurity the specialty areas that most align with my interests in cybersecurity are analysis, operations and maintenance, and protection and defense. The specific areas within those groupings that I am most attracted too are threat analysis, vulnerability assessment, incident response, customer service and technical support, cyber operations, and cyber operation planning. The categories that appeal least to me are investigations, governance, and security provisioning. Within these the specific areas that motivate me the least are criminal investigation, systems administration, executive leadership, software development, and system architecture. Despite my attraction or disinterest in the various areas listed in the source prompt I could see myself happily working in most of the areas outlined in the NICE Framework.
Journal Entry 2
Explain how the principles of science relate to cybersecurity
Cybersecurity should be studied through a social science structure since cyber and technology are human built and used architectures. These systems and technologies have become a major factor in how we function in our society giving merit to the importance of studying the affects on our populations and in turn how our populations are responding with new creations. Slide 3 of module 2 notes that Robert Bierstedt argued in 1970 that social sciences adhere to the same principles as the natural sciences. Some of the scientific principles that should be applied to cybersecurity when studying and researching are determinism, relativism, objectivity, ethical neutrality, parsimony, and skepticism. Properly examining data using these principals will ensure that challenges in digital security are fairly and equally examined for the best possible solutions that benefit all people.
Journal Entry 3
Visit PrivacyRights.org to see the types of publicly available information
about data breaches. How might researchers use this information to
study breaches?
The Data Breach Chronology is a tool created on PrivacyRights.org to assist researchers, journalists, policy makers, and advocates to interpret and make sense of reported digital information breaches in the United States. There are many different categories of data compiled together for sourcing research on who, why, what, where, and how intrusions occur across an array of industries. This website breaks down breaches by state, type of breach, organizations with the largest number of reported breaches, and breaches by organizational type. This information helps researchers understand the trends and bigger picture when looking at the cause and effect of these types of intrusions. Using this data people can search for possible solutions to keep information safe from criminal interests.
Journal Entry 4
Review Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and explain how each level relates
to your experiences with technology. Give specific examples of how
your digital experiences relate to each level of need.
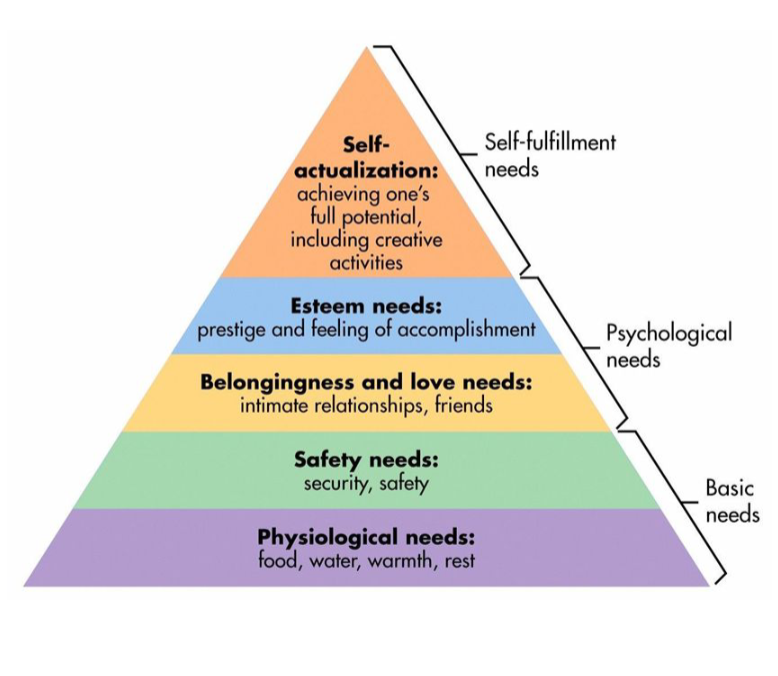
Abraham Maslow’s theory of the hierarchy of needs depicts all people as having needs that are hierarchal. The lower needs take dominance and once fulfilled a person seeks accomplishing the needs of the next level, slowly moving up the hierarchy.
My physiological needs of food, water, warmth and rest are met by going to work everyday and providing these basic biological necessities with pay. A way this level can be understood through my digital experiences would be through the necessity of digital work in my employment. I work in healthcare and log in repeatedly everyday through out the shift to access all of the digital systems that make my work possible. I also have to manage my digital accounts with various companies to ensure my water and electric bills are payed so I continue to have these resources and stay connected to the various utilities.
My safety needs of security and insurance are observed through the aspects of my life that provide perseverance. These needs viewed through digital experiences can be understood through the ways I use digital information to preserve my way of life. Some examples include using antivirus software, creating strong passwords, using a VPN for encrypted web use, and maintaining various insurances through online digital portals. Using these different services help ensure that my identity, finances, and computer systems which help me function in the world are working as intended for the best possible outcome.
The next level up in this hierarchy are my needs of belonging and love. These needs can be understood as needing to be a part of a community and want of deep social interactions. The ways in which I fulfill these needs digitally are through using communication devices, interactions on social media, contributions to discussion boards, and online shopping for gifts for loved ones. Utilizing cell phones and email are a couple of the digital ways that I take advantage of communicating with friends and family. Being understood and connected with the wider public are expressed through interactions on social media and discussion boards. Using ecommerce to source gifts to show my appreciation of loved ones are yet another example of fulfilling this level of need through digital technology. There are many ways to socialize digitally to gain rewards of love and affection.
Moving up this pyramid the next level is the need of self-esteem and feeling accomplished. This can be viewed as the ways I receive acknowledgment for my abilities and proficiency. Some examples of the ways I fulfill this electronically are by creating this ePortfolio to show my strong writing skills and understanding of complex concepts, posting on social media the successes in my life, and receiving positive feedback from responses that have been made online. Receiving positive feedback for my digital communications and work helps produce a feeling of competence and success.
At the top of this hieratical pyramid is the need of self-actualization. This can be understood through creative success that provides a feeling of achievement. Some electronic examples of this need are completing an online bachelors degree in the cybersecurity program at ODU, using my digital expertise for successes in providing education to my peers at work, and maintaining the digital policies, procedures, and job aids to keep staff in my work place following best industry practice providing an optimal patient care experience. Through completion of these various accomplishments it provides the feeling of capability and self-actualization by demonstrating my intellectual prowess and understanding.
In this increasingly digital world it is difficult to find aspects of my life that aren’t touched in some way by the digital experience. I rely heavily on electronic devices and systems more and more as new technologies and uses are developed. These innovations make tasks easier and allow for increasingly greater productivity. The loss of any of these systems or devices would induce anxiety in trying to find similar ways to fulfill these needs without the technical developments that have made accomplishment possible with less time and effort.
Journal Entry 5
Review the articles linked with each individual motive. Rank the
motives from 1 to 7 as the motives that you think make the most sense
(being 1) to the least sense (being 7). Explain why you rank each
motive the way you rank it.
Individual Motives
Individual Motive will depend on individuals and crimes.
1.
I think political motives makes the most sense as reasons to engage in computer hacking. If governments are repressing people and supporting inequalities the public may use the resources it has available to fight the oppression. This can be observed through the hacking of Parler to expose far right activists that engaged in questionable acts in repressing the democratic process by disrupting a peaceful exchange of power. This was also observed in Myanmar when protesters requested help from hackers to expose military contractor’s questionable activity which resulted in increasing sanctions from the international community and loss of support from major tech companies like Google.
• Political https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/magazines/panache/new-generation-of-angry-youthful-hackers-join-the-hacktivism-wave-adding-to-cyber-security-woes/articleshow/81707844.cms
2.
I rate the multiple reason article as second because there are probably many contributing factors that drive people to engage in this kind of criminal behavior. This article shares that money, power, and ego likely drives people to start these intrusion activities. Understand some of these different motives can give us help in preventing future attacks or persuading attackers to do good with their skills by helping companies find their vulnerabilities through penetration testing.
• Multiple reasons https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/what-drives-hackers-to-a-life-
of/?__cf_chl_jschl_tk__=pmd_c1d89a4695edbd23f2bceb54d70f35ce5e536e86-1626721164-0-
gqNtZGzNAfijcnBszQi6
3.
Next I would rate the recognition motive. Individuals that feel they have an immense amount of skill that is unrecognized and unacknowledged may try an attack that could give them wider attention fueling their ego and notoriety. This was observed when a UK hacker launched a DDoS attack against a British Labour party candidate which had a significant effect on the candidates ability to campaign in the election.
• Recognition https://www.theregister.com/2021/06/30/bradley_niblock_election_ddos/
4.
I would rate the money motive next. Prospects of wealth and a disposable income are a strong motivation to enlist in these destructive behaviors. People that are motivated by fancy spending, high stakes gambling, drugs, and prostitutes are more likely to employ themselves in cybercrimes. This article showed data that helped support this motive listing that hackers spent 20% of earnings on drugs and prostitutes, 15% went to buying fancy gifts to impress others, and another 30% went towards investments in properties and other high value goods.
• For money https://threatresearch.ext.hp.com/sex-drugs-and-toilet-rolls-how-cybercriminals-spend-their-money-infographic/
5.
I would rate the entertainment motive next because people sometimes attempt to complete certain task just to see if they can. A person scrapped Linkedin of 700 million public user data 92% of people using the service. The article explains that the individual responsible did it for fun, however, he is selling the data now, as well. This act took several months to complete because of its complexity. This hacker also scrapped Facebook of 533 million user data previously using the same techniques.
• Entertainment https://9to5mac.com/2021/07/19/man-behind-linkedin-scraping/
6.
Next I would rate the boredom motive from the provided articles. Children often engage with digital interfaces out of boredom. The provided article explained that there was a sharp increase in children using these interactive devices during the social restrictions of the COVID 19 pandemic. Criminal victimizers took advantage of this vulnerable population’s use of digital devices through, cyberbullying, grooming, and sexual abuse. The availability of vulnerable users created a breeding ground for an online victimization of children. I rated this above the revenge motive because targeting children and vulnerable people is major challenge that needs assessed. However, I rated it very low in this assignment because it doesn’t make any sense to me why people would want to victimize this population.
• Boredom https://www.heraldlive.co.za/news/2021-05-31-cyberbullying-and-online-sexual-grooming-of-children-on-the-increase/
7.
Finally I rate the revenge motive last because this motive was the cheapest and least rewarding. Psychopaths draw pleasure from abuse and misfortune. Using revenge porn and deep fakes to cause harm to victims is a despicable and trolling way to spend ones efforts. People that use this destructive means to attack others is the worst motivation for engaging in these crimes. It shows their motivations to create a dystopian malfunctioning culture that is fueled by anarchy and destruction.
• Revenge https://newsfromwales.co.uk/news/revenge-porn-victims-in-wales-often-feel-let-down-by-the-law-as-cybercrime-slips-through-the-net/
Journal Entry 6
How can you spot fake websites? Compare three fake websites (don’t
access those sites, of course) to three real websites. What makes the
fake websites fake?
Fake websites are used to catch users by disguising malicious websites to look like actual websites to prompt users to give away their personal information, download malware, and buy counterfeit products. They usually are built to look like the actual website, however there are a few ways to identify them. Check the domain name for misspellings or typos, look for extensions that look real but could be subverted, inspect the layout and design to see if it matches the real website, make sure there is https and a padlock symbol in the address bar which indicate a secure link, and always be cautious of requests for personal information.
Below are some examples comparing real websites from malicious ones.
Fake: www.amazonn.com
Real: www.amazon.com
The fake website in this example has a typo where an extra ‘n’ is used. Always check the spelling in the address bar to make sure it is correct. This is a common trick to fool users into thinking it is legitimate. The fake website also has a different layout, degraded image quality, and various spelling errors.
Fake: www.paypal-security.net
Real: www.paypal.com
In this example, the fake website uses a different domain name extension of .net instead of .com. This is another common subversion that fake websites use to trick users. The malicious site also asks for PII before logging in.
Fake: www.wikipedla.org
Real: www.wikipedia.org
In this instance fake website replaced the ‘i’ with an ‘l’ since they look very similar. This is another common way to fool users into using a fake website. This counterfeit site also has fewer links, old information, and pop-up advertisements.
Journal Entry 7
Review the following ten photos through a cybersecurity human systems integration framework.
Create a meme for your favorite three, explaining what is going on in the individual’s or individuals’
mind(s).
Explain how your memes relate to Human Systems Integration.
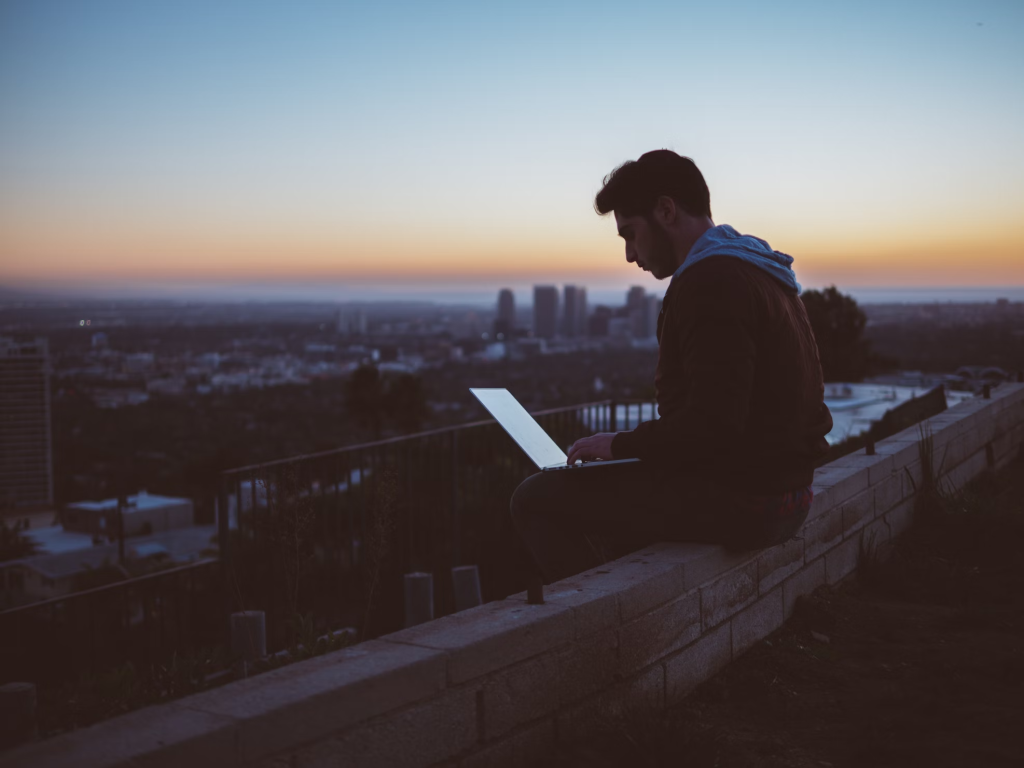

Cyber is everywhere!
The first meme I used I has the caption, “Cyber is everywhere,” because information systems are ubiquitous and have reached us everywhere in our culture. I used this image because it shows a person using a laptop on a roof. I felt that this image matched the message since it would not be expected that a person would pick such a place for computing, however, computing has reached us at virtually all places in the human experience.
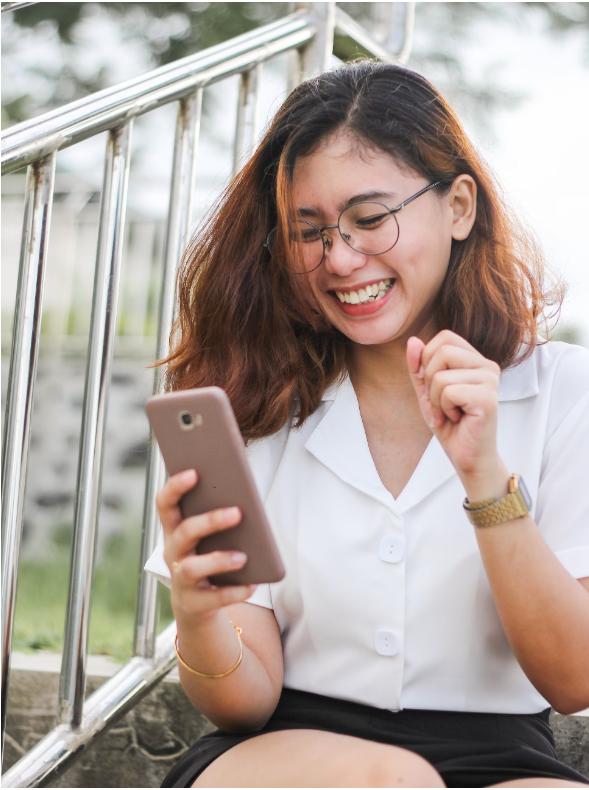

Social Engineering taking advantage of peoples emotions
The second meme selected shows a woman reacting with emotions of glee to something she is seeing on her personal cell phone device. The caption reads, “Social Engineering taking advantage of peoples emotions.” I felt this message matches the photo because social engineering is manipulating people through their emotional and intellectual vulnerabilities. If a hacker thinks they can trick someone through a psychological manipulation on their device they will try.
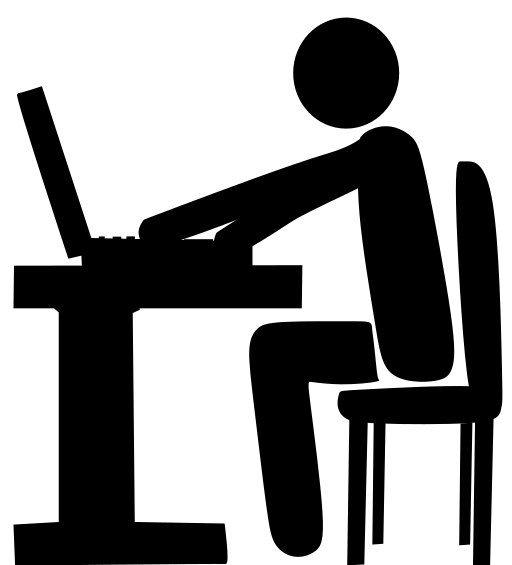

How are you vulnerable?
The third meme is a black stick figure using a computer with the caption, “How are you vulnerable?” I used this caption and image because if you use computers you are opening yourself up to endless vulnerabilities if you aren’t careful.
Journal Entry 8
Watch this video and pay attention to the way that movies distort
hackers. Hacker Rates 12 Hacking Scenes In Movies And TV | How
Real Is It? – YouTube
After watching the video, write a journal entry about how you think
the media influences our understanding about cybersecurity
The media attempts to attract viewers by creating the sensationalist content because this kind of content is a factor in what draws viewers in. However, another factor that attracts viewers is realism. They do want their depictions to be viewed as realistic because people seeing real applications in cinema is attractive in understanding of complex concepts use in the real world. In this video the speaker rates a series of popular content that depicts hacking through their plot and narrative. She rates various scenes on their realism and real life applications. She discusses how real life exploits are used in movies that describes similar intrusions that have happened in the real world like hacking competitions of capture the flag, using packet sniffers to observe traffic on servers, hacked government databases, use of hexadecimal code of how it is viewed and understood, and real life vulnerability hacks that have occurred on mainstream systems. The speaker also notes about science fiction predictions that have already come to fruition like the movie Hackers depiction of ransomware before their was real life instances of this attack and others that may still be developed fully in the real world like the mass hacking of autonomous cars. She does frequently allude to how media often takes liberties with how computer hacking is actually executed to add dramatization to their films. Some of the sequences where this added dramatization is used inflating the real hacking process are discussed in this video. In the move The Matrix, Trinity uses vinyl gloves while typing quickly is shown as unrealistic. In the movie Skyfall a scene is shown that uses dramatization in a digital forensic investigation using unsafe discovery techniques because it is easier to make the average user understand the concept they are trying to portray. Another example where the media takes liberties with real life exploits is seen in the movie Ocean’s 8 where an exploit device is used to crack passwords on computers. The speaker notes that this type of device is used for cracking cellular devices, however, it can’t be used to crack computer passwords that use a large number of characters because the large number of possible combinations would take more time and computational power than is currently available. In conclusion, the media attempts to make film as realistic as possible to make users believe their stories could be real life scenarios but do take a lot dramatized liberties to add suspense and reaction. This can deceive viewers about the possibilities of intrusion and their real life application if further context is not understood.
Journal Entry 9
Complete the Social Media Disorder scale. How did you score?
What do you think about the items in the scale?
Why do you think that different patterns are found across the world?
I rated very well on this scale with a score fairly close to zero. Every once and awhile I may experience a desire to or fell bad that the opportunity passed me by to use social media. However, for the most part I get little satisfaction from engaging socially digitally. I regularly see others struggle with the need for social online community.
I feel that the questions on this scale do a great job in quantitatively and summing up the draw many have to engage socially with others online. I’ve heard that this it is a big challenge for many people to control their social media usage. There is a variety of items on this scale which provides a good metric to assess addiction to this activity. I found it very telling that the questions sourced for this survey were pulled from a resources for Internet Gambling Disorder. People display similar feelings of reward and desire from online gambling and social media usage.
Different patterns of scoring from across the world might be evidence of how different cultures have distinguishable differences in what activities people use social media to avoid or start conflict over. From a cultural perspective, how and which applications users prefer could be based on what qualities different applications and platforms offer or whether or not they have a positive reputation. Some cultures embrace Facebook at a higher percentage, while others prefer What’s App. Some applications may be rated higher at how users can share personal photos while others may be better at how users can respond to comments. These differences might follow social norms in that some cultures hold higher value to specific designs than others. Another possibility is in which application becomes dominant first. People use these tools for community if no one in a community uses a particular application a user may change and use what the rest of their peers use.
Journal Entry 10
Read this and write a journal entry summarizing your response to the
article on social cybersecurity
https://www.armyupress.army.mil/Journals/Military-Review/English-Edition-
Archives/Mar-Apr-2019/117-Cybersecurity/b/
This article summarizes how information has become the newest battleground in warfare. This is attributed to how socialization and communication has become the dominant driving factor in societies of the modern day. This began aground the turn of the twentieth century with airplanes dropping leaflets and propaganda to change the hearts and minds of people and has progressed to the manipulation of our social networks and how we receive new information.
Russia has invested heavily on this new war of information launching blitzkrieg information warfare against their own people and adversaries trying to drive belief wedges wherever they can to advance their agenda. They are doing this using bots and misinformation to target topics and people that will help change public opinion of facts through what is believed politically and societally. These efforts use information to gain power and persuade the populace by targeting how people interact and respond to each other through changing opinions and public discourse.
Another example where information was used and shared that effected social cybersecurity were the changes to the power dynamics observed during the Arab Spring. This example shows that information has become decentralized making it harder for power structurers to control information and public opinions in specific countries. This event showed how quickly information technology and social media contributed to the changing of beliefs and support of multiple autocratic regimes allowing for their overthrow.
The efforts made to manipulate information to change public discourse is being completed through social-cyber maneuvering. This is accomplished as adversaries manipulate information and the network it is spread through. One of the ways this is being studied and understood is through the BEND forms of maneuver. This describes how the actor changes ideas, information, and the marketplace of beliefs through distortion, dismay, dismissal, and distraction.
The use of bots are being increasingly used as force multipliers to assist in manipulation and changing of beliefs. Bots are social media accounts that are automated programs used to move large informational transactions at scale. Bots can be used to drive positive and negative messaging depending on their purpose. These programs running accounts can automatically tweet, retweet, follow, friend, reply, quote, and like by persuading real users they are legitimate human members of their culture sometimes tricking them into believing misinformation.
This article does a terrific job of laying out the challenges facing social cybersecurity and the emerging war of information that is dominating the modern battlefield. Examples of this can already be observed with Russia’s information blitzkrieg and the Arab Spring power transfers. New tactics are emerging used in this new type of warfare including information maneuvering and the use bots. Lots of work and ideas are needed to combat these new forms of attack and misinformation to protect free peoples and preserve democracy.
Journal Entry 11
Watch this video. As you watch the video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iYtmuHbhmS0, think about how
the description of the cybersecurity analyst job relates to social
behaviors. Write a paragraph describing social themes that arise in the
presentation.
Cybersecurity analysts are the front line of defense when securing a network, which means they in a very social role within a organization. Many of the duties they are typically responsible for include working with employees or users who have experienced a breach like phishing attacks and intrusion attacks and the monitoring of the network by watching how users are utilizing the system. These roles assembled together could be understood as a cybersecurity help desk, meaning that good social skills and behaviors are a great quality needed in these positions. Another topic discussed in the video relating to social themes is negotiation of employment and geography. The speaker talked at length about moving to areas where cybersecurity analysts earn high wages. She shared the top 5 cities for pay which are in places that have high standards of living because of the competition to live there. This shows that high population density can result in higher pay and higher need for these positions. When negotiating for higher pay, having strong communication and socialization skills will benefit the applicant. Social themes are an important quality when seeking an analyst position due to their roles in assisting users, protecting a network, promoting proper cyber hygiene, the need to negotiate in obtaining positions, and working in population dense areas.
Journal Entry 12
Read this https://dojmt.gov/wp-content/uploads/Glasswasherparts.com_.pdf sample breach letter “SAMPLE DATA BREACH NOTIFICATION” and describe how two different economics theories and two different social sciences theories relate to the letter.
This sample breach notification letter is an example of what organizations send to users when their private information is compromised during a security incident within their network. This letter relates to two economic theories Rational Choice Theory and Laissez-Fare Economic Theory and two social science theories Structural Functionalism and Conflict Theory. Understanding these various theories and how they relate to a cyber security breach helps in understanding who is responsible for protecting user information, why attacks happen, and how to prevent future incidents from occurring.
Rational Choice Theory describes how users and businesses make decisions that will benefit their interests the most. This theory relates to this sample letter in that it describes what the organization is doing to recover their system and data to restore business function. It also explains what the users of the system can do to protect themselves from identity theft and fraud since their private information could have been compromised. Businesses and individuals prefer to make decisions that rationally give them the most protections and security.
Laissez-Fair Economic Theory can be explained as why the government shouldn’t interrupt economic functions except when protecting peoples rights. This theory is interrelated to this notification because it discusses how law-enforcement interrupted the organizations functions and became involved in investigating the breach. The breach delayed informing users of their data being compromised because of the needs of the investigation. Law enforcement want the best opportunity to catch or stop attackers to prevent continued and future breaches which could affect the rights of the public. They interrupted the communication and trust that the organization had with their clients so it could finish it’s investigation. This understanding of governmental oversite explains why there is a need to sometimes disrupt economic relationships to protect the rights of the public.
Structural Functionalism is understanding how society works through the components of it’s make-up. This theory is relatable to this breach disclosure because it explains how a third party platform provider that business functions were reliant, experienced an intrusion allowing unwanted access to private information. This letter explains to the users effected how an independent mechanism provided the vulnerability allowing for the security breech. Better understanding all factors that provide services to organization’s function can help determine where vulnerabilities exist and can be mitigated.
Conflict Theory is an interpretation of societal outcomes viewed through the differences in power and inequalities of society. Conflict theory relates to this breech notification by explaining what the attack compromised and how it occurred. The attackers broke through the organizations power structure to gain access to the private financial information of it’s users. This attack took place because a large amount of financial information was centralized in one location creating a vulnerability that adversaries would try and obtain access for financial gain. A large amount of resources available in one location provides opportunity for conflict when people want those possessions.
Comprehension of different social and economic theories can help organizations understand the vulnerabilities and motivations for attacks that could compromise it’s integrity. This knowledge helps in creating strong security policy and mitigating measures to protect stability and function. That awareness can be used to strengthen trust and security between businesses and their clients.
Journal Entry 13
A later module addresses cybersecurity policy through a social science framework. At this point, attention can be drawn to one type of policy, known as bug bounty policies. These policies pay individuals for identifying vulnerabilities in a company’s cyber infrastructure. To identify the vulnerabilities, ethical hackers are invited to try explore the cyber infrastructure using their penetration testing skills. The policies relate to economics in that they are based on cost/benefits principles. Read this article https://academic.oup.com/cybersecurity/article/7/1/tyab007/61684 53?login=true and write a summary reaction to the use of the policies in your journal. Focus primarily on the literature review and the discussion of the findings.
Bug Bounty programs are a resource that organizations can use to provide needed awareness of potential unrealized vulnerabilities that could compromise business function. This summary review of this article outlines the need for more bug bounty programs within companies with several helpful findings that depict how implementation can be obtained and is helpful. A vulnerability disclosure policy (VDP) should be in place for businesses that rely on cyber technology to provide protections from lawsuits for white hat hackers who find vulnerability flaws within a network. Research has shown that these policies are in place for only 25% of companies. This statistic has led the government to recommend the implementation of VDPs for all companies and government agencies. Some organizations have taken this recommendation a step farther by recruiting hackers directly to find these weaknesses.
The first finding explains that their is price elasticity to rewarding hackers for finding vulnerabilities. Companies that employ a bug bounty program have flexibility to paying hackers for this service because hackers are largely motivated by non-financial rewards. The second result of this study was finding that a company’s size and profile aren’t prohibitive for the number of reports it receives, showing that even small businesses can benefit from these policies. The third result found that finance, retail, and healthcare receive less reports than other industries. Perhaps showing that other incentives and recruitment should be made to shore up these short comings. The fourth finding shows that the number of bug bounty programs doesn’t dilute the number of reports received. This helps explain that as more programs are developed companies won’t see a decrease in vulnerabilities found. The fifth finding showed that as these programs age they receive less reports overtime. This finding can help explain why it can benefit organizations to change or expand the attack surface included in the program or offer higher bounties. The sixth and final finding shows their is a lot of work still needed because researched showed that more than 60% of variation within reports between data points of bounty programs isn’t understood.
This article’s findings explain the immense value for organizations in adopting a VDS and promoting bug bounty programs. Their isn’t a lot of evidence to discourage companies from participation based on their size or their resources available to implement these mitigating programs and policies. As these programs gain in popularity reports finding vulnerabilities will increase to meet demand. Some industries that lack participation in bug bounties should increase marketing for participation of these programs to help increase vulnerability identification. As the programs age, less reports are made requiring organizations to become creative expanding the attack surface or increase earnings of successful reports. There is still a lot of growth available in discovering the source of vulnerabilities that companies face. More research and studies are needed to determine the full extent of penetration testing needed for security.
Journal Entry 14
Andriy Slynchuk has described eleven things Internet users do that may be illegal. Review what the author says and write a paragraph describing the five most serious violations and why you think those offenses are serious.

The 5 most serious offenses from this list in my opinion are bullying and trolling, collecting information about children, faking your identity online, sharing passwords, addresses, or photos of others, and using other people’s internet networks. The 5 illegal things selected focus more on attacking users than on businesses which are more serious offenses because of lack of knowledge and protections they sometimes possess. Participating in cyberbullying and trolling is abusive behavior that can cause depression and self-loathing. These actions can have detrimental affects on the victim that can result in self-harm and suicide. Children shouldn’t be targeted online and shouldn’t be a part of datafication until they are consenting adults. Marketing has a large incentive to tracking generation alpha since they have only known a world with interactive screens, which allows them to be focused on and researched from a very early age. This creates a new unstudied and unknowable challenge since they don’t understand they are being persuaded and encouraged to taking certain actions. Faking one’s identity online is fraud. If users are pretending to be someone they are not this can compromise systems and data in many ways. If a person represents someone who they are not they probably shouldn’t be participating in the activity they are engaging in. Sharing people’s personal information online like addresses, passwords, and photos shouldn’t be posted without explicit consent. People have a right to privacy and protecting their information. If people post this information about others without their knowledge it is a breach of trust. People have a right to be forgotten and shouldn’t have to fight to stay anonymous from search queries and discovery. Individuals shouldn’t use other people’s networks without permission. This use of another’s resources is a form of stealing. People pay a lot for access to broadband from their internet service provider and shouldn’t have decreased bandwidth because of unauthorized use of their network. If a person commits illegal acts online on another person’s network it could put the owner in legal jeopardy. This unauthorized use can also put other devices on the network in peril because malware can transmit itself across devices on a network. These 5 illegal activities can harm others and should be mitigated whenever possible because of the damage they can do. The other 6 items in this list are crimes, cause harm, and shouldn’t be ignored either, however, they didn’t seem to meet the same level of seriousness.
Journal Entry 15
Digital Forensics wrt the Social Sciences
Digital Forensics | Davin Teo | TEDxHongKongSalon – YouTube Watch this video and think about how the career of digital forensics investigators relate to the social sciences. Write a journal entry describing what you think about the speaker’s pathway to his career.
In this video Davin describes his pathway to becoming an expert in digital forensics. His background was originally in accounting and through multiple job experiences and following his passion he worked through different IT and accounting positions and transferred into digital forensics. Emerging technologies are creating many previously unknown challenges and work for society. This profession was fairly brand new when Davin first applied and was hired into this field. He took advantage of a situation where there weren’t many candidates available with the needed career skills set. He capitalized on the need and lack of candidates and started working investigating cybercrimes. His story of hard work, passion, and opportunity lead him down a path that he had never knew existed. Having a perpetual drive for growth, continuing education, and interest in opportunity can lead individuals into fascinating and unheard of careers. His story is an inspiration for perspective candidates with an apatite for success and possibility.
Article Review 1
The reviews should focus on (1) how the topic relates to the principles of the social sciences, (2) the study’s research questions or hypotheses, (3) the types of research methods used, (4) the types of data and analysis done, (5) how concepts discussed in class relate to the article, (5) how the topic relates to the challenges, concerns, and contributions of marginalized groups, and (6) the overall contributions of the studies to society.
CYSE 201S_30075
Instructor: Teresa Duvall
By Adam Haas
2/10/2024
This journal argues that CSS (Client Side Scanning), despite possible benefits to law enforcement, has the potential to create major security and privacy risks that would have an effect on all of society. The article touches on sociological disciplines of criminology, psychology, and geography. This review highlights the sociological concepts discussed in the article concerning relativism, empiricism, objectivity, and ethical neutrality. The research completed for the article is archival research based on natural experiments which uses qualitative data to support its argument. This paper highlights the possible disparities to minorities and marginalized communities if CSS was implemented on all user devices. It also gives many examples of the different ways this technology could be subverted by user circumvention, hacked and weaponized by attackers, or could be used to target specific groups.
This technology has the potential to have a negative impact on marginalized and minority communities. This paper describes the phenomenon of distributional shift where false positives are to be expected because of differences in training data and real life data which tend to encourage errors disproportionately affecting minorities. It also highlights that scanning done on individual devices as opposed to a central server makes fairness harder to monitor. Another challenge that is noted is LGBTQ+ minors may have nude photos of themselves on their devices which could notify their parents of their identity before they are ready to come out. There are many ways that this software could disparagingly affect marginalized peoples intentionally and unintentionally depending on how it is developed.
This article does a great job evaluating and discussing the possible challenges that societies could face with the adoption of this type of technology. In theory, it offers a lot of benefits to policing and stopping illegal behaviors such as child abuse and exploitation, terrorist activities, and cyber victimization. However, the risks of such a system greatly outweigh the benefits. If attackers were able to infiltrate these systems they would have access to many new aspects of personal data and influence. The risks and opportunities that this level of surveillance could offer criminals and dishonest governments completely overshadow any benefits.
Abelson, H., Anderson, R. J., Bellovin, S. M., Benaloh, J., Blaze, M., Callas, J.,
Diffie, W., Landau, S., Neumann, P. G., Rivest, R. L., Schiller, J. I., Schneier, B.,
Teague, V., & Troncoso, C. (2024). Bugs in our pockets: the risks of client-side
scanning. Journal of Cybersecurity, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/cybsec/tyad020
Article Review 2
Article Review: “The Need for a Cybersecurity Education Program for Internet Users with Limited English Proficiency: Results from a Pilot Study”
By Adam Haas
Professor Duvall
March 23rd, 2024
This article outlines the need for a higher amount of attention to be invested in cybersecurity education for people who have LEP (limited English proficiency) to provide support for marginalized, disadvantaged minorities and to help protect the wider community’s cyber ecosystem. It attempts to extrapolate the extent of understanding that LEP individuals have regarding their safety in cyberspace. There have been few if any studies examining data and statistics researching the extent of cybercrime victimization of these people and communities. It discusses resources that are available for non-English speaking people and the ramifications of people engaging in unsafe cyber activities when there’s a dearth of understanding of cyber hygiene principles. This article outlines the experimental survey research that was conducted using a small pilot group of LEP people sourced from Hispanic and Vietnamese speaking communities using a pre-test assessment, educational modules presented in their native language, and a post-test assessment to better understand their cybersecurity proficiency, activity, and understanding. The concluding recommendations from the study are the creation of online resources for LEP people, creation of an online resource center in multiple languages, creation of an online LEP portal for cybercrime reporting, utilization of social media platforms as a resource for cybersecurity for LEP communities, and more assessment of impact of LEP online resources and education relating to cybersecurity practices. The article relates to many sociological concepts that have been presented in CYSE 201S that help make connections for why this is a challenge for all of society, not just people of the studied demographic.
Internet and computer-based crime is growing exponentially where every year more complaints are reported then the previous year. The amount of losses linked to cybercrime more than doubles each year since 2018 equating to over a trillion dollars lost annually at current levels. One of the best mitigating practices in the prevention of cybercrime is promoting education and awareness at the user level. Most instructive materials available for users are provided only in English. This puts people and communities where English is a second language at a disadvantage. LEP represents people who are older than the age of 5 and speak English “not well”, “not very well”, or “not at all”. LEP people are more likely to be non-native born and live in marginalized minority communities analogous to English-proficient people. LEP people make up 8.5% of the U.S. population mostly Spanish and Asian-language speaking. Human error is the number one cause of cyber victimization where lack of understanding and awareness contributes the most to this issue. When LEP people lack knowledge of how to protect themselves digitally it can erode the human firewall that protects all of society. Promoting and providing education to underserved communities protects everyone.
LEP people often live in marginalized communities due to their non-native origins that lack generational wealth and support. The language barrier disadvantages them in interactions with the rest of society, often preventing them from learning key information that could fortify their position and promote their upward mobility, and contribute to vulnerabilities associated with their safety and ability to report, respond, and prevent cybercrime. Language barriers of low-income, senior, and foreign-born/language-speaking residents result in a deficit of understanding of safe online behaviors and concepts that contribute to their susceptibility of cyberattacks.
The researchers studied this issue with a case study through an experiment conducted using field surveys consisting of a pre-test, education modules in the subject’s native language, and a post-test assessment. The data collected in this research is quantitative and qualitative. The quantitative research used precise demographics, technology use activity, and future intention questions to compare, contrast, and understand the issue better. The qualitative research consisted of a Q&A section in focus groups to better understand the participants’ situation and background to develop strong recommendations. The goals of this field study are to better understand the participants’ prevalence of cybercrime victimization, assess changes in their cyber safety behavior, and obtain feedback on the four presented educational modules on cybersecurity. The survey experiment was a pilot study that sourced subjects from Hispanic and Vietnamese communities in the Tampa Bay area to assess their understanding of cyber safety principles. The participants in this experiment consisted of three focus groups made of six Vietnamese, and 18 Spanish-speaking LEP individuals. All focus groups observed the same format and were guided in Vietnamese and Spanish. Subjects completed a pretest assessment followed by four educational modules on World Wide Web Cybercrime, Cyber Deviance, How to Stay Safe Online, and What To Do If You Become a Victim of Cybercrime. After the modules were finished participants completed the post-test assessment and joined a Q&A session. The pre/post-test questionnaires were geared to assess knowledge and changes in cybersecurity before and after being exposed to educational cybersecurity content. This study was limited in size and scope but offered valuable information about minority populations that rarely receive support and attention.
The research found that more resources need to be made available for non-English speaking people where cybersecurity concepts can be searched in their native language online. The subjects of this experiment rated all modules high relating to usefulness. Most of the participants revealed they intended to change their cyber behaviors to be more safe according to the pre and post-test results. All focus groups reported an urgent need for step-by-step instructional videos on utilizing security technology and learning how to perform certain tasks. These findings show the urgent need for more support and education of non-English-speaking people.
The recommendations of this study consisted of the following; the need for more online LEP resources, an online LEP resource center, an LEP cybercrime reporting outlet, utilizing social media as a cybersecurity LEP resource, and more research about the impacts of online LEP content. Education materials created should be presented in multiple formats providing content that is educational and entertaining to target the population’s literacy level, accompanied with a glossary of important web terminologies. One of the key recommendations from this article cites the need for a web application platform/resource center that provides content on cybersecurity and Internet safety in different languages. LEP people need a language-friendly way to report cyber victimization. The main outlet to report cybercrime in the U.S. is the Cybercrime Support Network’s website IC3, which has forms to report cyber victimization. However, this form is only provided in English, leaving already marginalized people behind. Another recommendation of the study is to make use of social media platforms that are popular with LEP populations in advancing an online resource center. The study’s final suggestion is to assess the impact of online material and resources on LEP individuals. This research should be ongoing to understand better the efficacy of the materials provided. The work should be continuous to protect non-English speaking people from cyber victimization. Attacks against these communities and individuals weaken and hurt the already marginalized and damage society as a whole.
This article relates to several sociological principles covered in CYSE 201S that help display how this research is needed for the whole of society. Relativism can be used to understand the challenges relating to the victimization of non-native, non-English speaking people. Immigration relates to cybersecurity in the need to have resources available for the language people speak so they can be functioning, contributing members of society. This article uses objectivity in its research by asking specific questions in the pre and post-test assessment and studying the results. The responses recorded give demonstrable findings about knowledge and the need for education regarding information technology safety. The research also holds how parsimony is applicable in LEP cybersecurity education. Computer and data science concepts need to be presented so they are understood at the target audience’s literacy level. Efforts should be made for comprehension for those with a foreign background who don’t have extensive education.
In summary, this journal article outlines the much-needed resources to educate LEP people about common security concepts and practices when utilizing information technology. The research completed in this pilot study shows that education is welcomed and needed to protect this vulnerable population. There is a deficit of content, research, and support to overcome these challenges which hurts already struggling communities and in turn, hurts society as a whole.
References
Ngo, F. T., Rustu Deryol, Turnbull, B., & Drobisz, J. (2024). The Need for a Cybersecurity Education Program for Internet Users with Limited English Proficiency: Results from a Pilot Study. International Journal of Cybersecurity Intelligence and Cybercrime, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.52306/2578-3289.1160
Cybersecurity Career Professional Paper
Select a type of cybersecurity career and write a two-page paper describing how professionals in that career require and depend on social science research and social science principles in those careers. Pay specific attention to the key concepts learned in class and demonstrate how those concepts are applied in the career you selected. The focus should be on demonstrating how the material from class relates to cybersecurity professionals’ daily routines. Specific attention should be given to how the career relates to marginalized groups and society in general. Students should use at least three reliable sources to write the paper.
Career Overview: Cybersecurity Specialist
Professor Teresa Duvall
Old Dominion University
By Adam Haas
April 6th, 2024
A crucial job in securing an organization’s information technology system and data is the Cybersecurity Specialist. This professional is responsible for ensuring that private information isn’t lost or accessed by unauthorized individuals. These jobs require social skills and understanding of sociological concepts to approach the human factor challenges that are vulnerabilities to information systems. This requires knowledge and research skills in social sciences to understand societal trends and the contributing factors of criminal behavior. This profession should be especially aware of security factors relating to marginalized peoples and the challenges they face in order to provide support for those who are underserved and lack protections. These jobs focus on reducing risks for companies in their work by protecting computer and information systems which prevent monetary losses and in turn emboldens the economy and benefits society at large.
A Cybersecurity Specialist needs good hard and soft skills to help secure organizations and to mitigate vulnerabilities. According to Indeed’s website (Cyber Security Specialist Job Description: Top Duties and Qualifications, 2023) candidates for this job should have computer, analytical, strong communication, problem solving, time management, and observational skills. These essential qualities are a mix of hard and soft skills and relate to how organizations are able to implement protections to fortify against risks. Professor Duvall (2024c) discusses in her Module 5 presentation the rich and diverse skill set needed for cybersecurity professionals of having a variety of skills hard and soft to be successful. Research suggests (University, n.d.), that Cybersecurity professionals and recruitment leaders need well-developed soft skills to accompany the technical hard computer skills required for securing an organization. Soft skill concepts are typically sociological because they relate to how people interact, solve problems, and understand each other. EC-Council explains (University, n.d.), that professionals need to be able to work within a team and efficiently communicate to strengthen relationships with employers, colleagues, and other professional relationships. Good technical computer skills should be coupled with strong social skills to ensure security analysis and mitigation strategies are a team effort where everyone is informed, involved, and proactively engaged in protecting the system.
Knowledge and understanding of human factors is essential for success as a Cybersecurity Specialist because humans are the central element in the security of information systems. Professor Duvall (2024) discusses in her Module 7 presentation the need for more training for cyber professionals to modify end-use behavior. People are the biggest vulnerability when securing and mitigating risks because of the challenges in understanding and managing behavioral based actions with the use of information technology (Nobles, 2018). These specialists must be able to understand people and motivations so they can think like an attacker to understand what is vulnerable and why. They should also be able to determine where the human weaknesses are and be able to communicate and educate about poor cyber hygiene, promoting security, and best practice. Human-enabled mistakes are due to over 80% of cyber attacks, data breaches, and ransomware attacks (Nobles, 2018). This highlights the need for Cybersecurity Specialists to possess excellent skills in managing human factors and understanding hard computer concepts.
Candidates for this profession should possess knowledge and understanding of using social science research to apply a scientific approach to mitigating risks and securing data systems. According to Bhattacherjee (2012), examples of social sciences include psychology the study of human behavior, sociology the study of social groups, and economics the study of firms, markets and economies, which are all a part of the sciences of people. These disciplines within social science all relate to the responsibilities that security specialists are expected to execute. Professor Duvall (2024d) expands on this interdisciplinary aspect of cybersecurity in her Module 1 presentation explaining how these social science disciplines intersect with this field by connecting these concepts with real world problems of managing and mitigating risks. These professionals should be able to think like a researcher using objective, empirical data to connect the dots of concepts and patterns to create generalized theories to why and how security concerns exist leading them to mitigating activities that will secure an organization’s digitized information (Bhattacherjee, 2012). Using research skills to understand the challenges that organizations face is instrumental in providing protections and staying objective in cybersecurity practice. Professor Duvall (2024a) discussed in her module 2 presentation the importance of objectivity as describing research in a manner that is value-free and empiricism as studying behavior that is real to the senses and can be studied. These skills will help specialists understand where benefits exist, where attackers are likely to infiltrate, and how human factors contribute to security so risks can be managed.
Understanding challenges relating to marginalized people should be understood by Cybersecurity Specialists due to the need to protect everyone and the lack of diverse representation in the cybersecurity field. According to Mountrouidou et al. (2019) diversity in cybersecurity is lacking, consisting of only 11% women, 6% African American, and 7% Hispanics. This underrepresentation of minorities is a difficulty in security because having a diverse workforce promotes having innovative organizational strategies in problem solving. Cybersecurity’s interdisciplinary nature of affecting a variety of disciplines requires professionals to have cultural awareness and ability to function with diverse interdisciplinary teams. Lack of diversity within cybersecurity is a challenge that heightens the need for professionals’ understanding of cultural differences and struggles of marginalized people to provide equal protections and support. Professor Duvall (2024b) discusses in her Module 3 presentation several reasons why diversity is needed in cybersecurity: different mindsets produce better decision making, promotes organizational growth, helps build tools to protect everyone, makes teams more innovative and productive, and helps guard against threats that target women and minorities. Her emphasis on diversifying inputs in approaching security shows how specialists need a well-rounded understanding of cultures and people. These specialists are benefited by cultural communication skills because the diverse population of the public are included in the human factors that are utilizing cyber resources. Cybersecurity subject matter is global, requiring professionals to understand concepts like unconscious bias that could lead to vulnerabilities in emerging threats (Mountrouidou et al., 2019). Cultural and diversity awareness helps support marginalized people, teamwork on interdisciplinary groups, and assists in the understanding of unconscious cultural bias. This awareness will help with that variety of diverse challenges that organizations face.
Cybersecurity Specialists need to possess a combination of hard and soft skills to excel in the variety of duties of this career. The soft skills are key social qualities needed for working with a variety of people and situations and are developed when pursuing this occupation due the interdisciplinary nature of securing information systems. These soft skills are highlighted with the challenges associated with human factors. The largest vulnerability that needs mitigation is the human element. Understanding sociological disciplines is crucial in understanding how they factor into and are interconnected with security concerns. These professionals should also understand cultural diversity and the challenges of marginalized people to provide support to those that are underrepresented. Cybersecurity has traditionally lacked diversity in its workforce resulting in unconscious bias in strategies affecting security. This lack of a diverse workforce puts greater pressure on professionals to approach work with an open mind and heightened cultural awareness so all people receive equal protection and understanding.
References
Bhattacherjee, Anol, “Social Science Research: Principles, Methods, and Practices” (2012). Textbooks Collection. 3.http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/oa_textbooks/3
Cyber Security Specialist Job Description: Top Duties and Qualifications. (2023, September 27). Indeed; Indeed. https://www.indeed.com/hire/job-description/cyber-security-specialist
Duval, T. (2024). Module 7: Cybersecurity and the Social Dimensions of Data Science (pp. 14–17) [Canvas: PowerPoint Presentation].
Duvall, T. (2024a). Module 2: Principles of Social Sciences and Cybersecurity (pp. 7–10) [Canvas: PowerPoint Presentation].
Duvall, T. (2024b). Module 3: Strategies to Study Cybersecurity through an Interdisciplinary Social Sciences Lens (pp. 31–34) [PowerPoint Presentation].
Duvall, T. (2024c). Module 5: Applying Psychological Principles of Cyber Offending, Victimization, and Professionals (pp. 24) [Canvas: PowerPoint Presentation].
Duvall, T. (2024d). Module 1: Introduction to the Social Sciences (pp. 21-23) [Canvas: PowerPoint Presentation].
Mountrouidou, X., Vosen, D., Kari, C., Azhar, M. Q., Bhatia, S., Gagne, G., Maguire, J., Tudor, L., & Yuen, T. T. (2019). Securing the Human. Proceedings of the Working Group Reports on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, ITiCSE- WGR ’19. https://doi.org/10.1145/3344429.3372507
Nobles, C. (2018). Botching Human Factors in Cybersecurity in Business Organizations. HOLISTICA – Journal of Business and Public Administration, 9(3), 71–88. https://doi.org/10.2478/hjbpa-2018-0024
University, E.-C. (n.d.). Why Soft Skills Are Key to Success in Cybersecurity. EC-Council University. https://www.eccu.edu/blog/cybersecurity/soft-skills-cybersecurity-professionals/