Splign is a tool provided by NCBI that uses an algorithm to determine gene duplications, introns and splice signaling. Its primary input is cDNA (complimentary DNA) which is aligned to an unspliced genomic sequence. If you do not have a genomic sequence which is unspliced splint provides the whole genome for some more common species such as human, cow, mouse, etc.
From the output you can gain insight as to the transcription start site, exon lengths and position, transcription termination site, and alignment of the sequence.
Input: cDNA and genomic sequence
Output: The output is primarily visual annotation of exons and introns within the scope of the provided cDNA sequence. This allows manipulation in other programs that require this data.
Using Splign:
We will be performing our evaluation on the online version of Splign however, there is also a download link if you wish to work with it onboard on your computer
First, we will head over to the Splign site : Splign
and click on the online link at the top
from here we will be asked to put in a cDNA sequence as well as a genomic sequence
Our example we will be using silkworm cDNA and genome input files.
our silkworm cDNA/mRNA file is as follows:
>Silkworm mRNA sequence
GAAACTGCCATAGTTTTGCTACTTACTACTACTGGGTACCTACCTATTTAATTACGTTTTCACATAAAGA
GCTATTAACTCGTAGTTGTAATTCCTCAATTATAACACTGTTTTAACATTATAAAACCATGGGAGTCGAC
GTGGAAACTATTTCACCTGGAAATGGATCAACTTACCCAAAACCGGGCCAAACTGTAGTCGTTCACTACA
CTGGAACGTTACAAAACGGAAAGAAATTCGATTCATCTCGAGATAGAGGGCAACCTTTTAAATTCACATT
AGGCAAAGGTGATGTCATAAAAGGATGGGATCAAGGATTAGCAAAGATGTCTGTAGGGGAAAGAGCGAAA
TTGACGTGCTCTCCTGACTTTGCCTATGGTTCCAGAGGCCACCCAGGTGTAATACCACCAAACGCTACTC
TAATTTTTGACGTTGAACTCTTACGTGTTGAATAATGTTTATTGATTGAAAAACATTCGGGCCTTAAAGT
TTTTACAAGATTCTTCATAAAAAAAACCACTTATGCCCACAAATCTAAATCGTATTATTTATTTTGTTTA
ATAGTTTTATATTTTACAGTGACTTAAAAATACATGTGATAAAATAATATGTACATAATATTTAATTGAG
GAGTACAACCTCGGCTTAGG
Lastly, click the align button at the bottom to produce your results
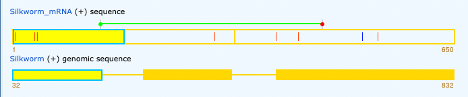
Below we can see our mRNA produced 3 exons that align with our genomic file. There are a couple of red lines in our exons which indicate a different nucleotide in the cDNA than provided in our genomic file. We also see a blue line in the 3rd exon indicating that a nucleotide is absent from the genomic sequence where one exists in our cDNA file. The green line above the exons shows the actual start and end of transcription of amino acids in the sequence.
Our first exon shows 3 single variants in our alignment. Also we can see where amino acid transcription begins on the second line accompanied by an M, Methionine.
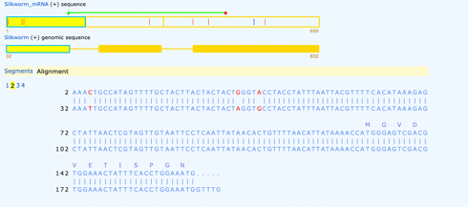
The second exon shows complete transcription throughout, this is not always the case as transcription may not always start on the first exon. Here we see one variation labeled in red.
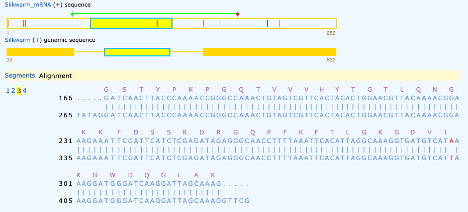
The third exon provides us with the transcription stop site labeled by an * in the amino acid position, as well as three variations (seen in red) and an additional nucleotide found in the cDNA which was not specified in the genomic DNA (seen in blue).

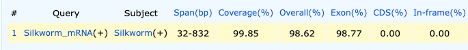
Further evaluation can be done via the text link to the right side of the page. This link will show a table, as seen below, with the length of the transcription sequence, start and stop sites for the cDNA (Q, Start and Q. Fin) and genomic DNA (S. Start and S. Fin)

