Journal Entry #1
Within the Government and Awareness role category, Cybersecurity Instruction interests me the most. It is gaining popularity globally, with high demand for jobs due to the rise in cybercrime, which is expected to grow in the coming years. Cyber instructors are responsible for developing and conducting cybersecurity awareness, training, and education programs. I am interested in this role because it involves passing on crucial knowledge to those aspiring to join the cybersecurity field. On the other hand, the Cybercrime Investigation role appeals to me the least. Investigating cyberspace intrusions and crimes is tedious and time-consuming, and a large percentage of cybercrimes go unsolved. This lack of resolution and the challenging nature of the work makes it less appealing to me.
Journal Entry #2
Cybersecurity ensures that researchers separate personal biases from data analysis. Favoring simpler explanations, parsimony aids in understanding human behavior in cyber incidents. Empiricism provides a foundation for cybersecurity research by relying on data from surveys and experiments to build reliable knowledge. Ethical neutrality is vital, requiring adherence to ethical standards and protecting participants’ privacy when studying sensitive topics like online surveillance. Determinism suggests that prior events influence behavior, helping us understand hacking tactics while recognizing human choice. Finally, skepticism is crucial, demanding that all claims about cybersecurity threats be critically examined for accuracy and potential biases. These principles of science collectively offer a comprehensive understanding of cybercrime and guide effective prevention strategies.
Journal Entry #3
According to the website privacy.org, researchers can utilize the comprehensive dataset provided by the Data Breach Chronology to analyze data breaches in the United States. This includes identifying trends over time, understanding the most prevalent types of breaches (such as hacking and insider threats), and recognizing the sectors that are most vulnerable (such as healthcare and finance). By delving into breach specifics and notification details, researchers can evaluate the efficacy of current security measures and strategies for responding to data breaches. This valuable resource can be crucial in shaping policy decisions and directing efforts to enhance data security across various industries.
Journal Entry #4
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory that suggests human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, with lower-level needs needing to be met before higher-level needs can be addressed. Technology has significantly impacted how we fulfill these needs. For example, technology can help us meet basic needs like accessing food, water, and shelter through online grocery shopping, food delivery apps, and weather information apps. It also provides security features like antivirus software, firewalls, and password management tools to protect our devices and data. Additionally, technology facilitates social connections, helps us achieve goals and gain recognition, supports personal growth, and helps us find meaning and purpose in life. In conclusion, technology has become an essential part of our lives, drastically fulfilling our needs at every level of Maslow’s hierarchy, from basic survival to self-actualization
Journal Entry #5
When it comes to the motives behind cybercrimes, several factors come into play. Financial gain stands out as a primary driver, with many cybercrimes motivated by the desire for monetary profit. Second on the list is Revenge, it’s another significant motive, as personal vendettas can lead individuals to commit serious crimes. Additionally, the rise of hacktivism illustrates the growing trend of using hacking for political or social causes, highlighting its importance as a motive. Seeking recognition and validation within the hacker community also drives many individuals to carry out high-profile attacks. Although less common, boredom can lead individuals to engage in harmful online behavior due to a lack of positive outlets. While some hackers may act for entertainment, the severe consequences make this motive less compelling. Lastly, the motive of multiple reasons is complex and encompasses various motivations without clear prioritization, making it a vague and multifaceted factor in cybercrimes.
Journal Entry #6
Identifying Fake Websites
Here are three examples of fake websites and their real counterparts
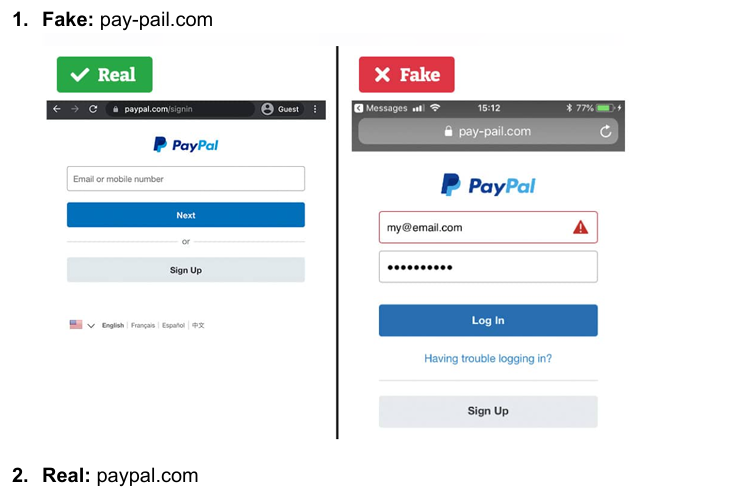
Differences:
Domain name: The fake URL contains a typo in the domain name,” pay-pail”
• Website design: The fake website has a different layout.
• Content: The fake website contains incorrect or misleading information, such as
fake contact information or login pages
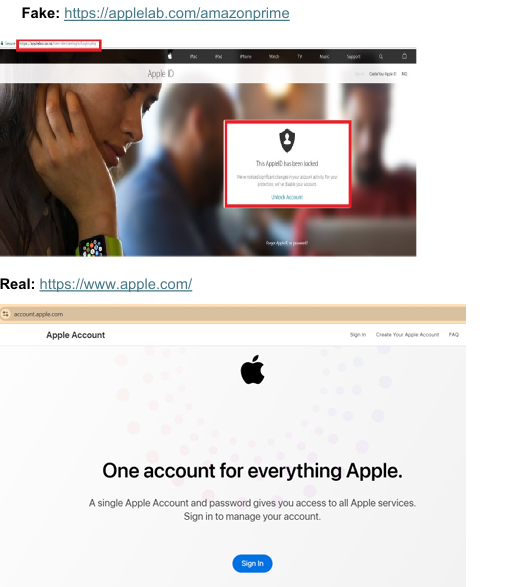
Differences:
• Domain name: The fake URL omits the “www” subdomain.
• Website design: The fake website has a different logo or layout, and the content
may appear suspicious or low-quality.
3. Fake: https://www.amazonn.com/ 3.Real: https://www.amazon.com
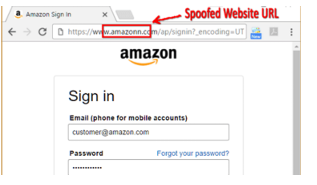
Differences:
• Spelling and grammar: The fake website may contain spelling or grammar
errors.
• Contact information: The fake website has incorrect or suspicious contact
information.
• Suspicious links: The fake website may contain links to malicious websites or
phishing scams.
Journal Entry #7

Explanation: When the system asks you to change your password to something more
secure, but you can’t remember it, it’s a common struggle to remember complex
passwords. Using easily guessable passwords like “doggy123” can compromise
security, while overly complex passwords can be difficult to remember and may lead to
users choosing weaker alternatives.
Was it Doggy123 or
D0ggy123!

Explanation: The individual is a victim of a phishing scam due to a lack of awareness
or critical thinking. Phishing attacks exploit human tendencies, like greed, curiosity, and
fear of missing out. The excitement felt from getting the latest phone overpowers her
judgment.
Can’t Wait to get my free
iPhone 16 Pro Max

Explanation: Teachers are teaching while students’ attention is elsewhere. Part of
cybersecurity is studying human behavior. Just as a bored student might not retain
knowledge, an employee who finds security measures irrelevant may bypass them.
When the professor is
explaining encryption, but your
busy decrypting memes.
Journal Entry #8
Media’s Influence on Cybersecurity
After watching the video, it’s clear that the media often distorts the reality of cybersecurity and hacking. Movies and TV shows tend to dramatize hacking, making it seem more glamorous and instant than it truly is. For example, in shows like Mr. Robot and The Matrix, hacking is often portrayed as fast, visually engaging, and reliant on flashy, unrealistic interfaces. This misleads the public into thinking cybersecurity is simple, rather than the complex, meticulous process it is. Hacking involves careful planning, patience, and knowledge of systems, as security expert Keren Elazar points out in her critique. The media’s portrayal can sometimes trivialize the risks and real-world consequences of cyber-attacks, making it seem like a game rather than a critical, evolving issue. This inaccurate depiction could impact public awareness and understanding of cybersecurity threats.
Elazari, K. (2021, March 16). Hacker rates 12 hacking scenes in movies and TV | How real is it? [Video]. YouTube. Insider. https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=6BqpU4V0YpkLinks to an external site.
Journal Entry #9
Reflecting on my score of 0 on the Social Media Disorder Scale, I recognize that my cultural background in Trinidad and Tobago influenced my relationship with social media. Social connections here prioritize in-person activities like hanging out and playing games, so while social media is used, it doesn’t dominate our interactions. My generation, especially the Class of 2017, grew up emphasizing outdoor activities and face-to-face time with loved ones, leading to a more moderate influence from social media. This cultural context reduced our dependency on social media for connection or validation, contrasting with the current generation’s deeper integration of these platforms into their daily lives.
Journal Entry #10
Social Cybersecurity – A New Frontier
The article on social cybersecurity presents an insightful perspective on the evolving landscape
of information warfare. It underscores the increasing sophistication of cyberattacks that target
not only systems but also individuals and societies.
A significant takeaway is the distinction between traditional cybersecurity and social
cybersecurity. While traditional cybersecurity focuses primarily on technical vulnerabilities,
social cybersecurity explores the psychological and social dimensions of cyber threats. This shift
highlights the necessity of understanding human behavior and social dynamics in the realm of
cybersecurity.
The article’s examination of Russia’s information warfare strategies is particularly noteworthy.
By employing tactics such as disinformation, propaganda, and social engineering, Russia has
illustrated the potent effects of information operations that can influence elections, create
discord, and undermine trust in democratic institutions.
To effectively tackle these challenges, organizations and individuals should adopt a multi-faceted
approach that integrates technical measures with social and psychological strategies. These
strategies include:
1. Digital Literacy: Educating individuals on online security best practices, including
recognizing and avoiding phishing attacks, misinformation, and disinformation.
2. Critical Thinking: Fostering critical thinking and media literacy skills to help people
assess information and identify biases.
3. Strong Cybersecurity Infrastructure: Implementing robust technical measures to
safeguard systems and data from cyberattacks.
4. International Cooperation: Collaborating with other nations to establish international
norms and standards for responsible state behavior in cyberspace.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, it is crucial to remain informed about the latest
trends and tactics employed by cyber adversaries.
Journal Entry #11
In the video “What Does a Cybersecurity Analyst Do?”, Nicole Enesse emphasizes the crucial role of cybersecurity analysts in protecting systems and data. A key takeaway is the importance of strong communication skills, as analysts must collaborate with various departments to ensure security measures are understood and followed. This requires the ability to simplify complex concepts for non-technical staff, highlighting teamwork and patience.
Additionally, analysts need to stay up-to-date on emerging cyber threats and understand the human behaviors that cybercriminals exploit, illustrating that cybersecurity is as much about social dynamics as it is about technology.
Journal Entry #12
The data breach notification letter from GlasswasherParts.com illustrates the interplay between economic and social theories in consumer-business relations. Information asymmetry is a key concept here, as GlasswasherParts.com and its platform provider were aware of the breach while customers remained uninformed for months. This lack of timely information could economically harm customers if they continue using compromised payment cards.
Additionally, externalities reveal how one party’s actions can negatively affect others. For example, customers may face unexpected costs and stress due to the company’s security shortcomings, underscoring the need for businesses to invest in preventive measures.
Trust theory highlights the importance of consumer confidence; the breach and delayed notification have eroded trust in GlasswasherParts.com. The letter attempts to rebuild trust but may leave long-lasting doubts about the company’s commitment to data protection. Lastly, social responsibility theory posits that companies have an ethical duty to safeguard public interests. The emphasis on cybersecurity efforts and cooperation with law enforcement in the letter reflects an effort to fulfill this obligation. Together, these theories demonstrate how data breaches impact economic and social dynamics, influencing business practices and public expectations around digital security.
Journal Entry #13
Bug bounty programs are an innovative approach to cybersecurity where companies reward ethical hackers for identifying vulnerabilities in their systems. A study I reviewed highlights the effectiveness of these programs as a cost-efficient security measure, particularly for companies that may not have the resources to employ full-time penetration testers.
One key takeaway from the study was that security researchers, motivated by intrinsic factors such as recognition and problem-solving, are often less reliant on monetary rewards than one might expect. This allows companies to benefit from these programs even on a limited budget. However, the research also noted challenges, such as the diminishing number of valid vulnerability reports as these programs mature. This suggests that companies need to continuously adapt and expand their code bases to maintain the effectiveness of their programs.
While sectors like finance and healthcare reported fewer vulnerabilities, the difference was not statistically significant, raising interesting questions about sector-specific challenges. Overall, bug bounty programs appear to be a valuable tool for enhancing cybersecurity, especially when tailored to the specific needs and maturity levels of companies and their respective industries.
Reference
Sridhar, K., & Ng, M. (2021, March 12). Hacking for good: Leveraging hackerone data to develop an economic model of Bug Bounties. OUP Academic. https://academic.oup.com/cybersecurity/article/7/1/tyab007/6168453?login=true
Journal Entry #14
The Five Most Serious Internet Violations
Andriy Slynchuk highlights five illegal internet activities with serious ethical and legal implications: using unofficial streaming services, torrenting, cyberbullying, collecting data on children under 13, and extracting copyrighted content from YouTube.
Unofficial streaming services and torrenting violate creators’ intellectual property rights, causing financial harm and stifling innovation. Cyberbullying can result in severe emotional distress for victims. Collecting data on children under 13 without parental consent violates the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA) and poses risks to vulnerable populations. Additionally, extracting copyrighted content from YouTube breaches copyright law and the platform’s terms of service.
These activities damage individuals, creators, and the digital ecosystem, emphasizing the need for ethical online behavior and stringent enforcement of internet laws.
Reference
“Children’s Privacy.” Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC), https://epic.org/issues/data-protection/childrens-privacy/#:~:text=The%20Children’s%20Online%20Privacy%20Protection%20Act%20(%E2%80%9CCOPPA%E2%80%9D)%20specifically,and%20was%20revised%20in%202013. Accessed 16 Nov. 2024.
Slynchuk, Andriy. “11 Illegal Things You Unknowingly Do on the Internet.” Clario, Clario Tech Limited, https://clario.co/blog/illegal-things-you-do-online/. Accessed 16 Nov. 2024.
Journal Entry #15
Davin’s story highlights the dynamic and impactful nature of digital forensics, moving beyond the stereotype of a purely technical career. His journey demonstrates how this field combines global exposure, human behavior, and high-stakes problem-solving.
Davin emphasizes that his work goes beyond “white lab coat” environments, addressing real-world issues like insider threats in companies involved in illegal activities such as piracy, embezzlement, and even fraud. The role of a digital forensics investigator represents a unique intersection of technology and social sciences, where analysts interpret technical evidence while considering the societal and psychological contexts of cybercrimes to uncover the truth behind digital footprints.
Notably, Davin’s experiences align with Routine Activity Theory, as many incidents he described involved clear motives and a lack of guardianship, creating an environment conducive to crime. Additionally, Organizational Culture Theory comes into play, particularly in cases where entire IT departments were complicit in unethical activities, highlighting how workplace culture can foster or prevent wrongdoing.