Assignment:
Explain how to principles of science relate to cybersecurity.
Answer:
In this journal I will be explaining how the principles of science relate to cybersecurity. First we need to understand that social sciences adhere to the same principles as natural sciences, as Robert Bierstedt (1970) had argued. In conclusion this means that social sciences are just as scientific as natural sciences. In this context the principles of relativism, objectivity, parsimony, empiricism, ethical neutrality, and determinism can be applied to cybersecurity through the social science framework.
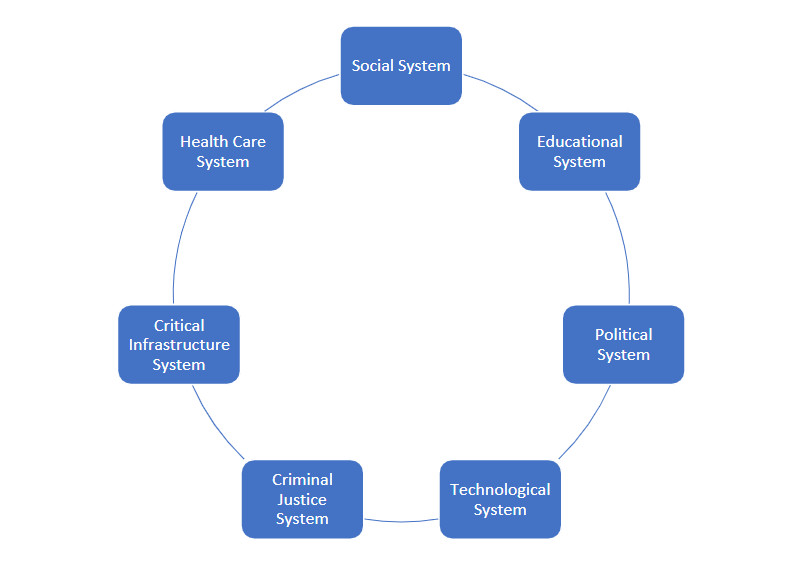
In the context of cybersecurity and social sciences, relativism can be understood to mean that everything is related. For example changes in one system will lead to changes in other systems. Regarding cybersecurity, relativism plays a role in systems like educational systems in which they rely on technology more and more each day. This leads to a demand in a heftier understanding in cybersecurity to insure that sensitive and/ or confidential information does not get leaked. We are required to understand how broader technological changes influences behavioral dynamics, economic decisions, policy making, and social processes, when understanding cybersecurity through a social science lens. Few of the most connected systems to cybersecurity are shown below and relativism encourages us to recognize that changes in any of these systems lead to changes in cybersecurity.
The principle of objectivity says that science does not exist to promote an opinion or a point of view, instead it exists to advance our knowledge based off of facts only. It is important for those who study cybersecurity to stay objective when researching a topic. This can be challenging, especially if the topic being researched awakens strong emotions in the researcher. For example the question of how we understand the promotion of white supremacy in the digital world touches on a subject that we all have a strong opinion on. In topics like these the task for social scientists is to stay objective so their opinion is not shaped by their opinion.
Parsimony, as a principle of science, means that scientists should keep their level of explanation as simple as possible. Keeping explanations as simple as possible ensures that others understand the explanation and test the explanations in subsequent research. It is also important to keep explanations as simple as possible so others who are not as knowledgeable in cybersecurity can understand why it is important to have good cyber hygiene and not to ignore it.

As a principle of science empiricism means that social scientists can only behavior which is real to senses, i.e. behaviors which relate to touch sight, taste, hearing, and smell. This mean that scientific knowledge comes from that which we experience. We can see this in cybersecurity quite often. For example when scam e-mails became more frequent we were taught how to handle a situation in which we had received one. Social scientists agree that knowledge in our disciplines must come from empirical research, meaning we cannot, and should not, rely on our opinions to frame our understanding of cybercrime and cybersecurity. Doing so could lead to erroneous conclusions and will have little value in the science community.
Ethical neutrality refers to the fact that scientists must adhere to ethical standards when conducting research. This includes protecting the rights of the study subjects and willing to study topics empirically and objectively. This also goes for cybersecurity because we cannot just hack into someone’s computer without their knowledge to perform research. This intrudes on the subjects right to privacy and therefore neglects ethical neutrality.
Determinism is a principle of science in which it is described that behavior is caused, determined, or influenced by preceding events. There are two models of explanation within a determinism framework: The nomothetic model, which identifies the relatively few causes of a behavior, and the Idiographic model, which identifies the multiple causes over time of a behavior. In cybersecurity an example of both of these models would be a cyber incident. One example would be to ask why someone commits internet fraud and you would try to think of preceding events that could have influenced this decision. For example a person who is looking for quick money could hack into someone’s bank account. However social scientists do not believe that behavior is 100% determined by preceding events.