Mobile Device Security
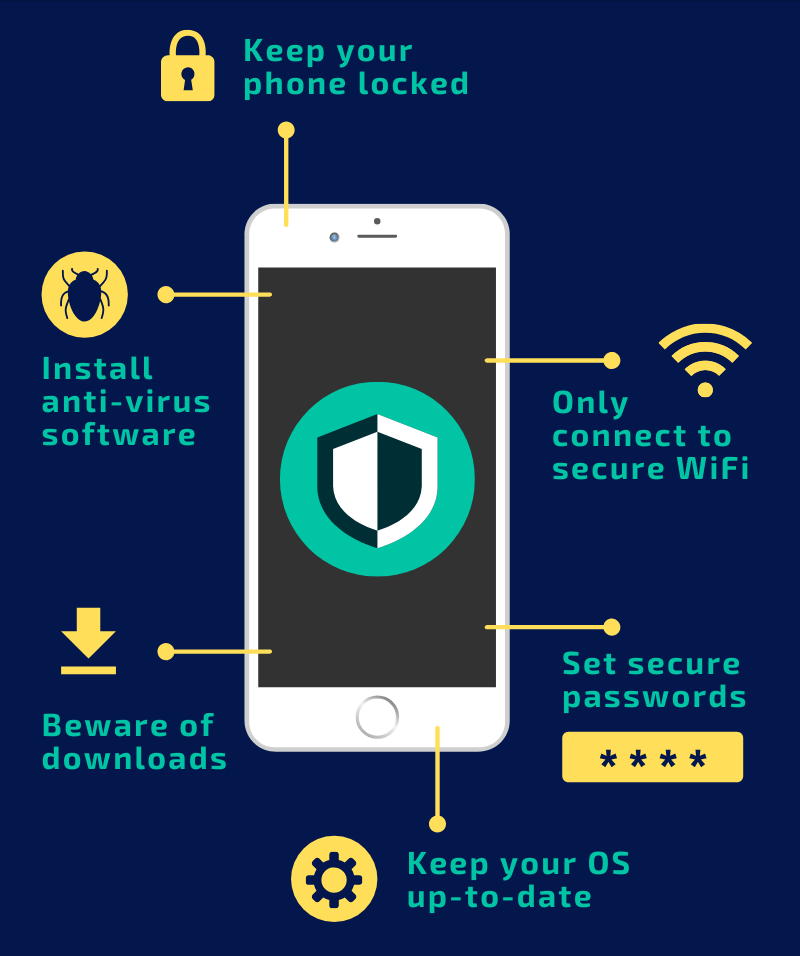
As mobile devices such as phones, smart watches, tablets, and other related gear have become more pertinent in the modern cybersecurity landscape, for both personal and business use, it is equally important to protect these machines with the same level of care as traditional, non-mobile systems have been in the past. With these tools being an essential part of daily communication, work, data storage, and more, these devices have become increasingly more target by malicious actors. Mobile Device Security as a cybersecurity concept involves protecting mobile devices against threats such as malware, phishing / vishing attempts, SIM swapping, and other various forms of attacks that would negatively impact both an organization or individual who is affected. Strategies formed to protect against these threats include multi-factor authentication (MFA), mobile antivirus software, accessing sensitive or work material through a Virtual Private Network (VPN), only connecting to trusted and known WiFi, using biometric based authentication (something you are), automatic software updates, and more.
Identity & Access Management (IAM)
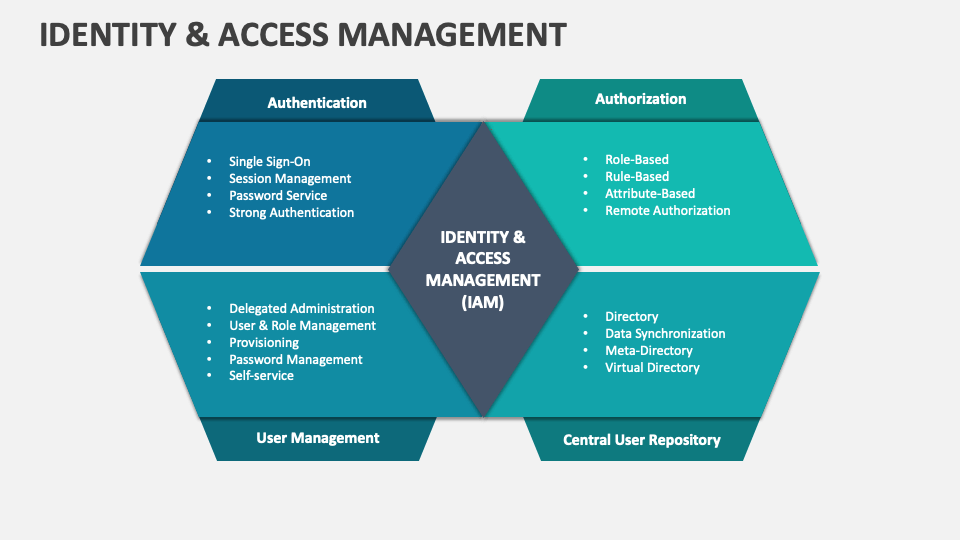
Identity & Access Management (IAM) is an approach and framework centered around ensuring that only authorized individuals, pre-defined groups, and roles can access the desired resources at the correct time. This policy helps to protect organizations and agencies from insider threats, unauthorized access to material, data breaches, and overall helps to reduce the risk faced by an entity by protecting the integrity of their systems and data. IAM does not stand alone, as it is influenced by and works alongside various government regulated compliances such as HIPPA or GDPR to ensure compliance with access to data and how it is stored. Some features of Identity & Access Management include multi-factor authentication to protect against unauthorized access even in cases where a malicious attacker have obtained a password, Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to limit those with a certain role to only be able to access the bare-minimum of necessary information in order to complete their job, as well as enforcing strong password policies to help prevent successful password based attacks.
Vulnerability Management
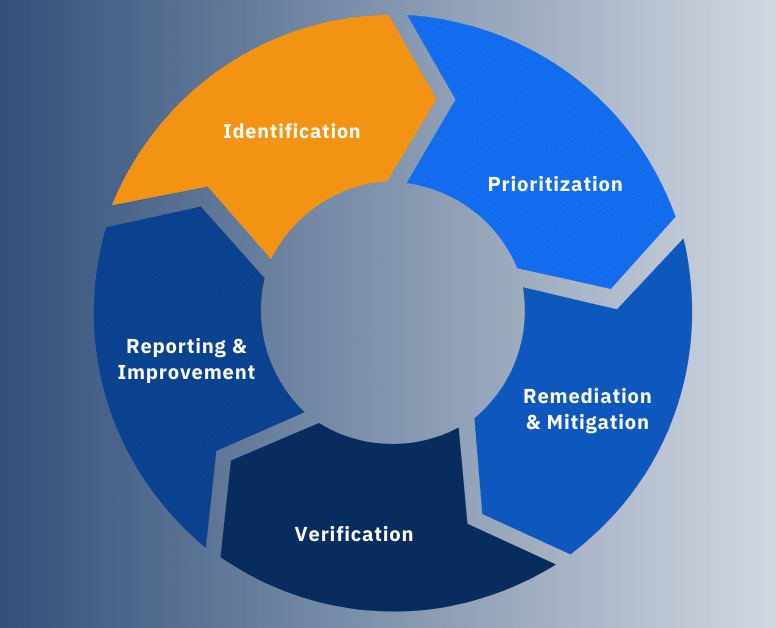
Vulnerability Management is an ongoing process in which businesses, organizations, and various entities continuously identify, prioritize, and remediate vulnerabilities in an effort to mitigate the overall risk faced across the groups attack surface. When done correctly, vulnerability management will minimize the possibility of a successful attack and allows the IT team to have a clear view of the systems, software, prioritizations, and policies in place that are being constantly monitored by automated processes alongside manual ones as well. Some examples of the tools, software, and processes used during vulnerability management include:
- Nessus
- OpenVAS
- VPR
- Ivanti
- Microsoft Defend Vulnerability Management
The Vulnerability Management lifecycle is displayed below: