Spotting Fake Websites
Oftentimes when navigating the internet, we are left with only our best judgment to mitigate malicious users from harming our systems and accessing our data unauthorized. One way that malicious users gain access to our systems is through the websites we connect to over the internet.
What are some telltale signs that a website is fake or suspicious?
1: An Invalid SSL Certificate or Insecure Error
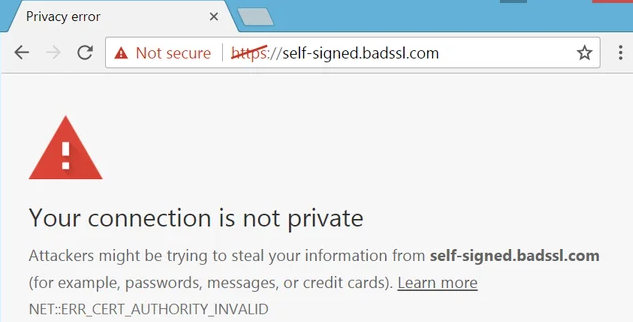
(Fitzgerald, 2024)
Fitzgerald, A. (2024, January 5). A simple explanation of SSL Certificate Errors & How to fix them. HubSpot Blog. https://blog.hubspot.com/website/fix-ssl-certificate-error
When accessing a fake website, you can expect to come across an error that warns the users of its invalid SSL Certificate and that the connection to the website is not encrypted; leaving the connected computer vulnerable to a middleman hacker.
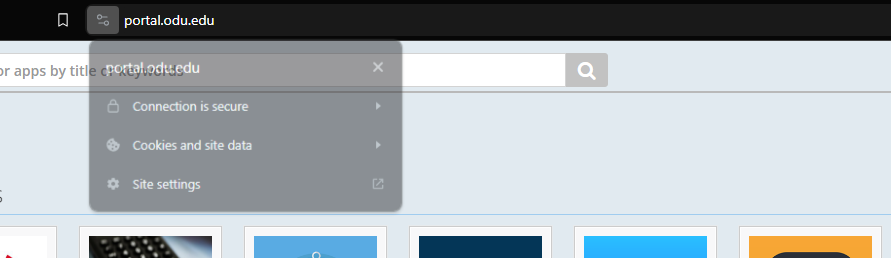
A trustworthy site (in our example the Old Dominion student portal) displays a secure connection and a valid certificate of authenticity.
2: A Lack of Contact Information
When visiting online shops, it is a good decision to check if the site owner has left any contact information or an About page. The website I have in this example was actually removed and only snapshots are available through the online WaybackMachine.
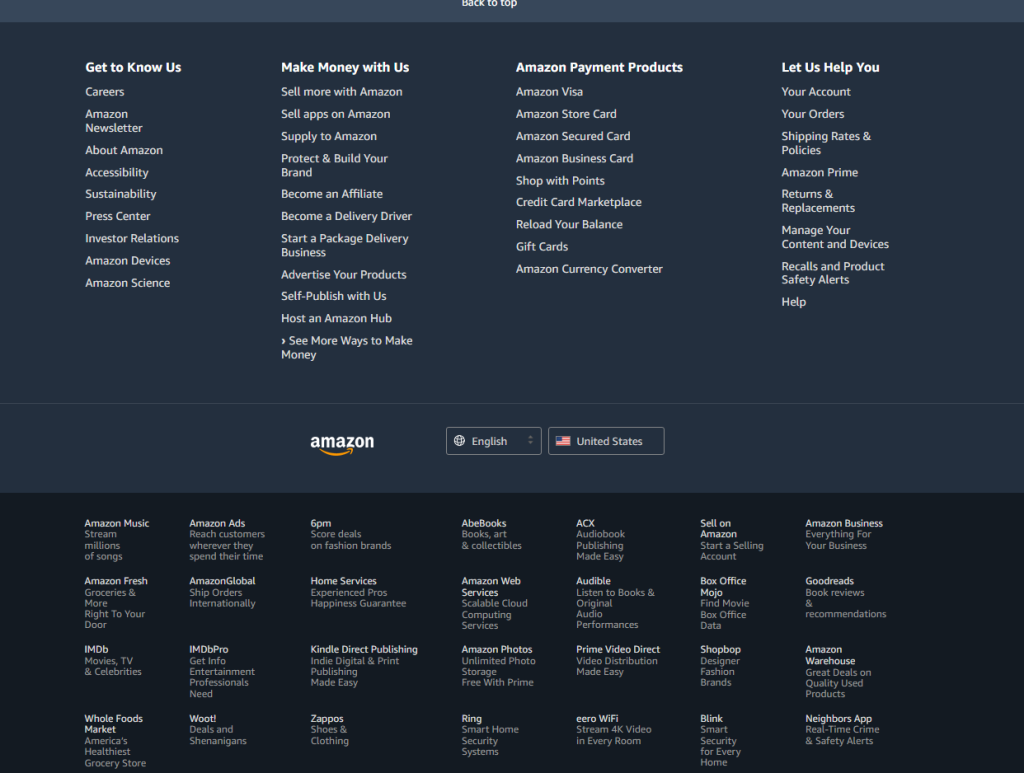
Amazon being a well-known and trusted site has many links to get in contact with various teams throughout the business.
3: Often Originate from Spam Emails or Strange URLs
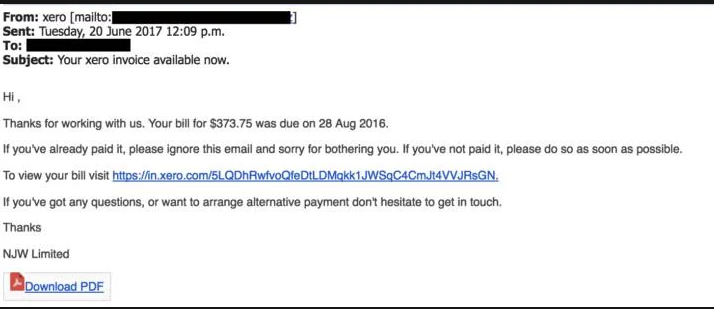
(Woods, unsecure)
Another way a malicious user can get you to access a fake website is through phishing emails and asking for account and billing information.
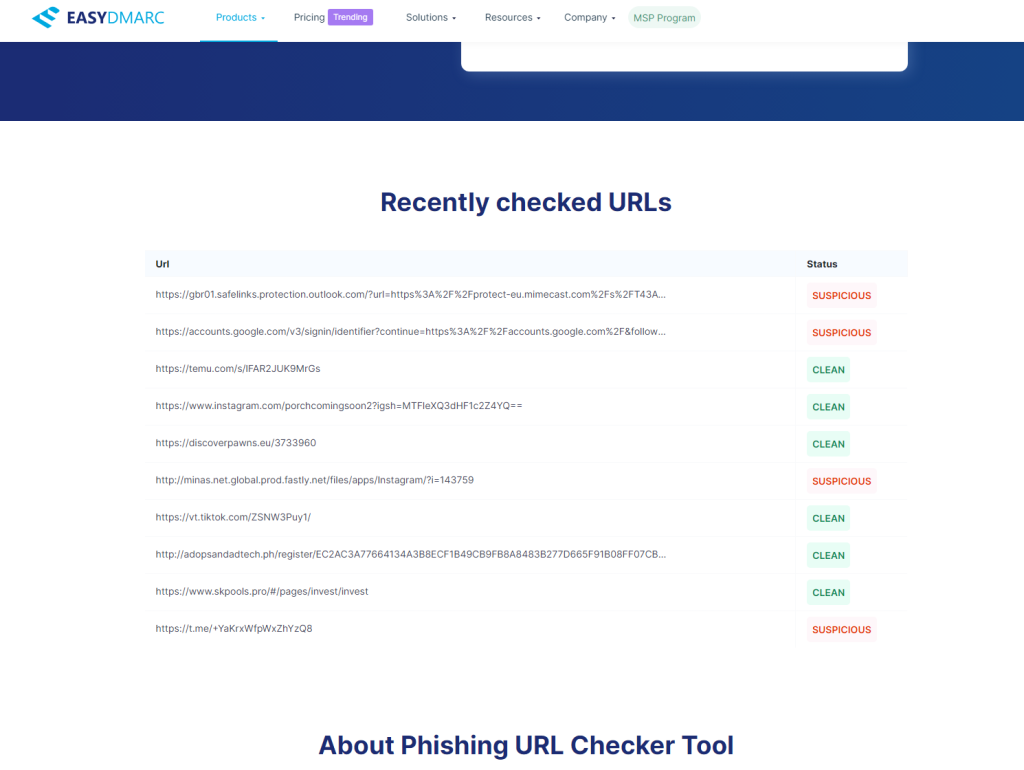
Phishing link and URL checker. EasyDMARC. (n.d.). https://easydmarc.com/tools/phishing-url
When in doubt, search the internet for any suspicious connections to the URL.
