Fats
The three main contributors of fats in mashed potatoes are milk, cream cheese, and butter. Milk contains myristic, stearic, and palmitic acids. Butter and cream cheese contain mostly oleic, myristic, and palmitic acids.
- Myristic acid – 14 carbons, saturated, nonessential
- Stearic acid – 18 carbons, saturated, nonessential
- Palmitic acid – 16 carbons, saturated, nonessential
- Oleic acid – 18 carbons, mono-unsaturated, omega-9, nonessential
The most common fatty acid between all of these foods is palmitic acid, pictured below:
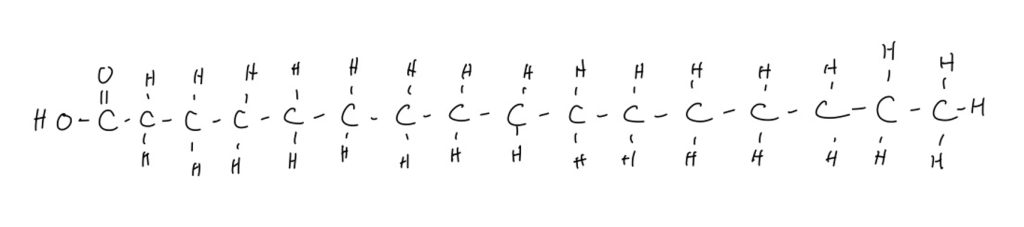
Carbohydrates
The main source of carbohydrates in mashed potatoes is the starch in the potatoes. There is also carbohydrates in milk in the form of lactose. These are both natural sugars.
Protein
The main source of protein in mashed potatoes is milk. There are 8 grams of protein per cup in whole milk. Milk is a good source of the amino acid leucine.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamin D (from milk) – Good source, 10%
Calcium (from milk) – Excellent source, 20%
Vitamin A (from milk) – Good source, 10%
Potassium (from potatoes) – Excellent source, 20%
Iron (from potatoes) – Good source, 10%
