The monoclonal antibody, otherwise known as -mAb, Bapineuzumab helps treat the disease Alzheimer’s. Alzheimer’s is a neurological disease that deteriorates motor functions over time and causes memory loss (Mayo Clinic, 2024). This happens as a result of the brain shrinking and eventually starts to lose brain tissues and cells. Additionally, this illness is progressive, which means that it worsens with time. Expanding on some symptoms of Alzheimer’s like memory loss and deterioration of motor functions, it may also cause behavioral changes. For example, a person with Alzheimer’s may tend to be more aggressive or may not have the same personality traits that they once had. Alzheimer’s can also affect a person’s psychological state of mind making them more paranoid and often making them experience hallucinations. There are usually 3 stages to Alzheimer’s, and they include mild, moderate, and severe. The mild stage includes problems like “wandering and getting lost, trouble handling money and paying bills, [..] and personality and behavior changes” (National Institute on Aging, 2023). In the moderate stage, damage can occur in regions of the brain responsible for language, logic, and sensory processing. This includes the ability to detect sounds and smells. And finally, the severe stage of Alzheimer’s is where “plaques and tangles spread throughout the brain, and brain tissue shrinks significantly” (National Institute on Aging, 2023). In terms of genetics, there is more than one hereditary component to Alzheimer’s. It is more likely that it is controlled by several genes together with environmental and lifestyle variables. One of the main causes of Alzheimer’s is the plaque caused by amyloid beta.
Moving from Alzheimer’s disease, Bapineuzumab is one of the few treatments for this disease and helps researchers gain knowledge about it. Bapineuzumab is an lgG class of antibody and “targets the N-terminal region of Aβ”, otherwise known as amyloid beta, (Martin R. Farlow, 2013). When senile plaques assemble, it binds extracellularly to Aβ. When infused “the drug acts as passive immunotherapy against Aβ plaques” (Martin R. Farlow, 2013). The medication’s effectiveness and safety were examined in multiple clinical trials. This treatment was first developed by Élan and Wyeth and went through many phases of clinical testing. In those phases, overall safety and tolerance were established and a trial “tested four doses of the antibody or placebo in patients with mild-to-moderate [Alzheimer’s] who were either carriers or noncarriers for the [Alzheimer’s] risk-factor allele, ApoE4” (H. Crehan, 2016). Post analyses showed cognitive benefits in the ApoE4 noncarriers, thus allowing the advancement of bapineuzumab into more trials. The reason why Bapineuzumab works so well is because it binds to the amyloid beta. As stated before, one of the main causes of Alzheimer’s is the plaque buildup because of amyloid beta. By attaching itself to the N-terminus of amyloid beta in both its soluble and fibrillar forms, Bapineuzumab lowers the concentration of amyloid beta in the brain. This also helps stabilize plaque levels caused by amyloid beta. Another feature of Bapineuzumab is that it also helps with memory loss.
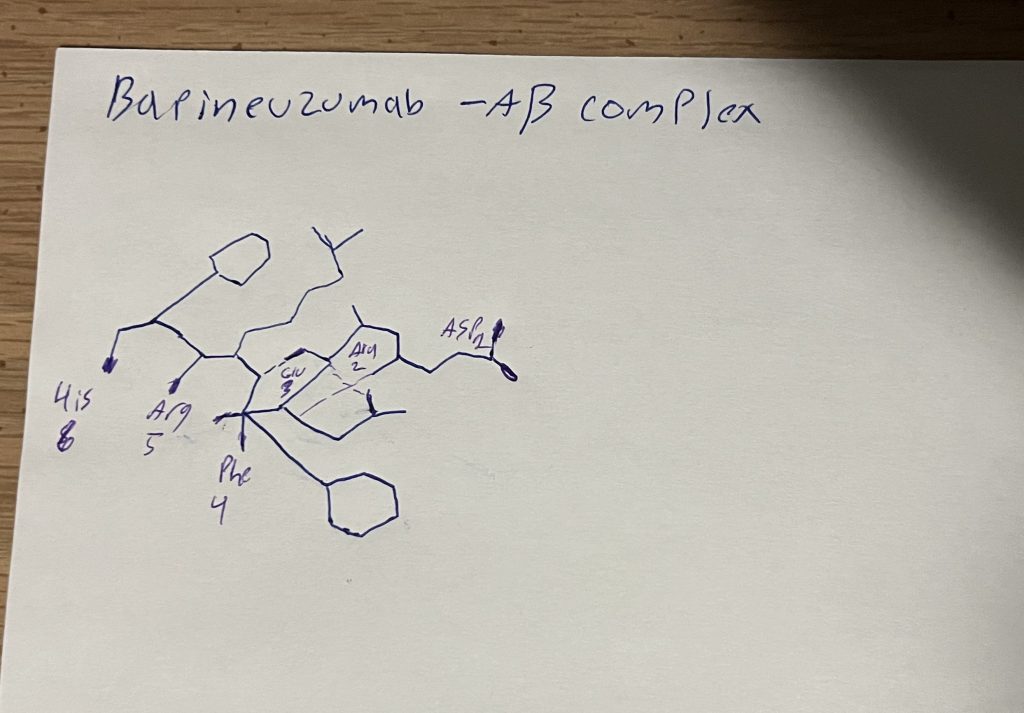
Bapineuzumab structure
References
Alzheimer’s disease fact sheet | National Institute on Aging. (n.d.). https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-and-dementia/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet
H. Crehan, & AbstractAlzheimer’s disease (AD) currently affects 44 million people worldwide. (2016, June 3). Anti-amyloid-β immunotherapy for alzheimer’s disease. Developing Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128021736000071
R. Farlow MD, Holmes, C., Sperling, R., Farlow, M., Jaturapatporn, D., Games, D., Schenk, D., Bayer, A. J., Gilman, S., Vellas, B., & Orgogozo, J. M. (2013, May 18). Immunotherapy for alzheimer’s disease. Neurologic Clinics. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0733861913000388
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2024, July 10). Alzheimer’s disease. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alzheimers-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350447

Leave a Reply