Scada Systems
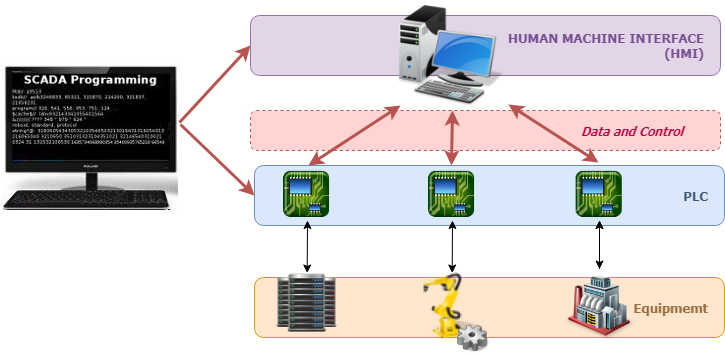
The success of any organization, industry, or entity relies mainly on its system implementations. One of such systems is Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA). Which according to an article by scadasystems.net, “is an industrial control system (ICS) that is used to control infrastructure, facility-based, or industrial processes such as water treatment, wastewater treatment, airports, spaces stations, manufacturing, production, refinery and power generation respectively” (scadasystems.net,2021).
The concept of SCADA is primarily to monitor and control an operation from a centralized system, often within a large area or site. There are subsystems within SCADA that help in its successes, such as the type of apparatus used, which humans mainly operate with access to all data, also known as the Human Machine Interface (HMI). There is also the supervisory system which is responsible for the gathering of data about the process. Moreover, the Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) and the Communication infrastructure work together to ensure the operation’s success. It should be noted that the SCADA systems process does not control in real-time, but rather it coordinates the process in real-time by sending command controls to the process. The components of SCADA are hardware and software, making it possible for organizations to control their processes from anywhere remotely. Prior to the use of SCADA, many systems would have people at every stage in the process, such as running a ship’s energy. At every significant point of the energy room, there would be sailors physically turning buttons, pulling plugs, or turning on knobs for the ship’s room to function. However, the use of SCADA has made it simple to reduce the number of human presence due to the software that can coordinate the systems. Such functions are previously controlled by humans on the ground to be monitored and controlled by just clicking on a centralized computer system, a tablet, or even a phone.
The use of SCADA by organizations in industries such as power producers, water and waste management, and some manufacturing companies have experienced tremendous growth and efficiency in their daily operations. SCADA has made it possible for these organizations to receive real–time dates and alerts that can help with the smooth running of their process. Just like most smart systems, SCADA systems are not immune to attacks. On the contrary, increasing cyber-attacks on SCADA systems result in costly damage to the organizations that use them. According to a publication by Security week, “there was an incident in which occurred in March, where cybercriminals used unknown ransomware to target a water facility in Nevada, and the malware affected SCADA and backup systems. However, the agencies noted that the SCADA system only provided monitoring and visibility capabilities, and it was “not a full industrial control system.” (Kovacs,2021). SCADA systems are vulnerable to different forms of attacks; hence it will be prudent for organizations to implement systems that will help in mitigating these attacks and securing any vulnerabilities associated with the SCADA system.
SCADA systems since its inception have contributed significantly to increased production and ensuring quality and on-time delivery of services across major industries. However, there is still work to be done to reduce the numerous attacks on SCADA systems as technology increases daily.
References
Kovacs. E. (2021). Security Week: Ransomware Hit SCADA Systems at 3 Water Facilities in the U.S. Derived from https://www.securityweek.com/ransomware-hit-scada-systems-3-water-facilities-us
SCADA systems. (2021). SCADA Systems: SCADA Systems concepts. Derived from