Cybersecurity Tools and Methods
The goal of this page will be to illustrate free tools that are available online and ways that they can used to better understand cybersecurity principles. Additionally, these tools are immediately actionable, and their uses will be documented in the following illustrations and explanations. This page be utilizing information and methods laid out by the following book:

Essentially, Cybersecurity identifies and deals with threats that an organization (could be a business, government, or country) might come in contact with. This traditionally looked at with the CIA Triad Model.
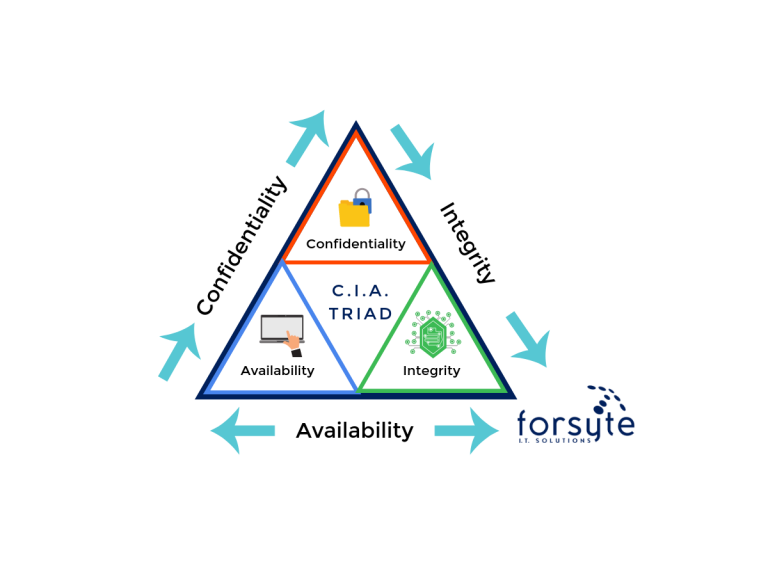
The meaning of this three-word acronym is straightforward; the implementation of the principles is where the nuance lies. Confidentiality deals with the protection of data and assets that an organization deems only certain parties should be privy to. Integrity is the principle that said data and assets should only be capable of being changed by those with proper authorization. Finally, the Availability principle states that all data and assets should be readily available when needed by the relevant parties. The model of a triangle is not accidental. Focusing too much on one of the three principles will cause the other two to concede their power, thus threatening the integrity of the overall structure.
Black Hat Methodology
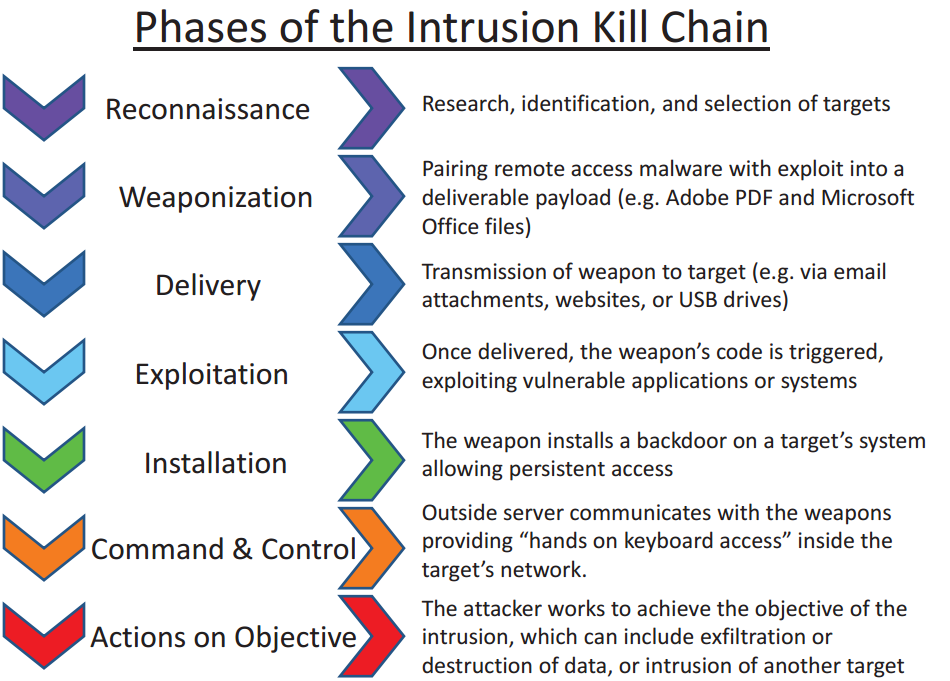
An example of what a black hat might follow is the Lockheed Martin Cyber Kill Chain (or CKC). The image below will illustrate the order and goal of each step.
Pinging
A simple way to determine if you have a connection to a destination is to use a ping test on the command line.

Shodan
Shodan can be utilized either thorough a package that can be installed through the command line, or through a browser at https://www.shodan.io/
Shodan allows you access a plethora of publicly-available information. For example, Shodan allows you to list systems that still use the default password for access.
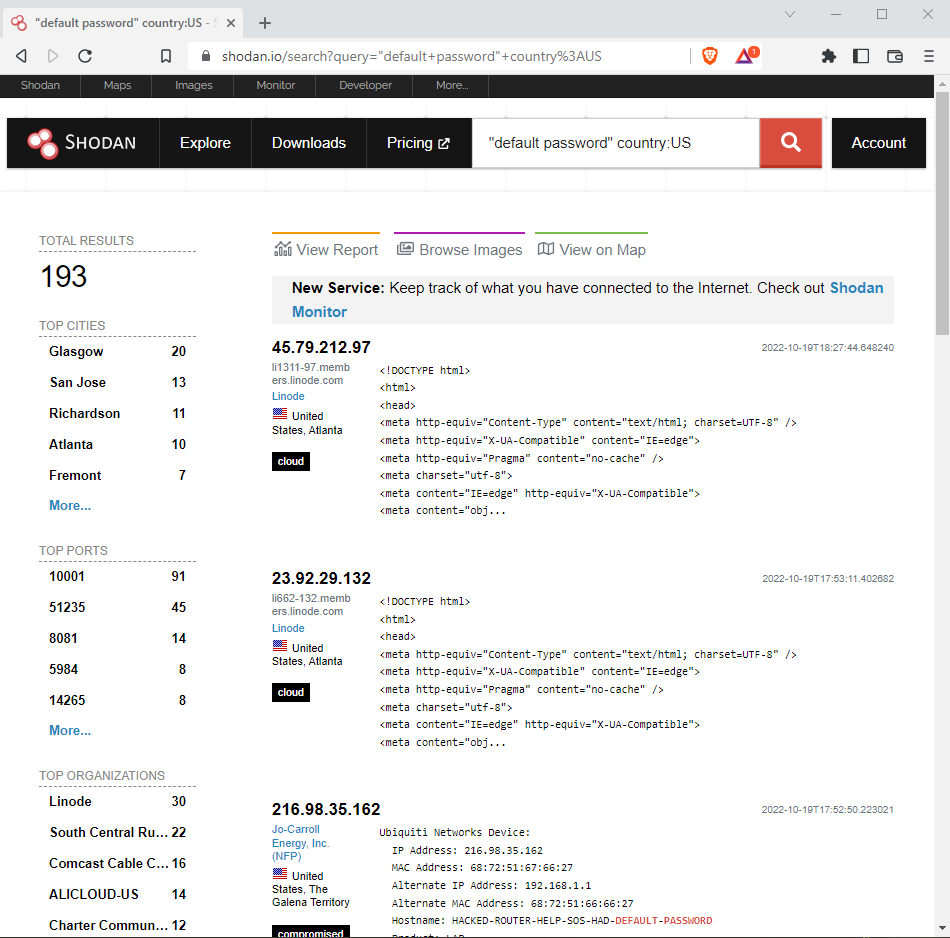
Again, this is public available information.
