This assignment was to find an example of a monoclonal antibody used in medicine today, summarize the condition that this drug treats, Identify what class of antibody it is (sketch of the structure was advised), and explain what this antibody is binding to (or thought to bind to) and how that should improve disease symptoms.
Alemtuzumab
Conditions That Alemtuzumab Treats
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody medication primarily used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS), an autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system. MS occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, known as myelin. This leads to inflammation, demyelination, and a range of neurological symptoms. The treatment process typically involves a course of intravenous infusions over several days, followed by monitoring and potential additional courses as needed. Alemtuzumab is often considered for individuals with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS), a subtype characterized by periodic exacerbations of symptoms followed by periods of partial or complete recovery. Clinical trials have shown that it can significantly reduce the relapse rate and slow down the progression of disability in some patients. However, Alemtuzumab is not without risks. It can lead to various side effects, including infections, infusion reactions, and autoimmune disorders. Therefore, its use is carefully monitored, and patients require ongoing medical supervision. Alemtuzumab is also used for treatment in patients who have B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL). After a patient has been given alkylating agents, such as bendamustine and chlorambucil, and have negative or no results from fludarabine they are administered Alemtuzumab. Alemtuzumab is usually administered intravenously into the bloodstream, but you may also have it subcutaneously injected under the skin. Some doctors also use Alemtuzumab in stem cell transplants to reduce the risk of a certain complication called graft versus host disease.
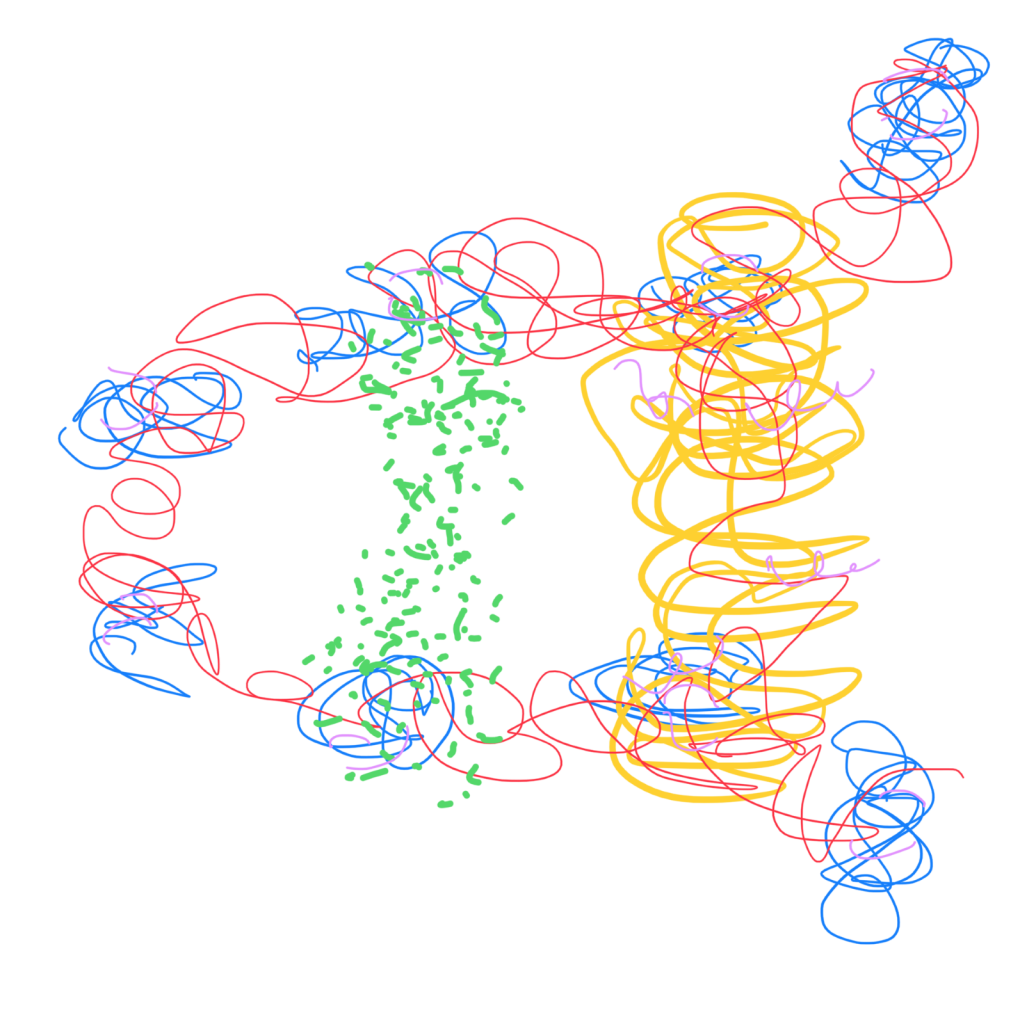
This image is a the Structure of IgG1 B12 heteroterotetramer. The blue part represents the two heavy chains. The gold part represents the two light chains. The green dots represent the glycation.
How Does Alemtuzumab Work?
Alemtuzumab is a monoclonal antibody used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and some types of leukemia. It works by targeting and binding to a protein called CD52 on the surface of certain immune cells, primarily B cells and T cells. Alemtuzumab specifically binds to CD52, which is a protein found on the surface of a mature lymphocyte but not on the stem cell that they come from, receptors on the surface of immune cells. Once bound to CD52, alemtuzumab triggers the destruction of these immune cells through various mechanisms, including antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). This process leads to the depletion of B cells and T cells. By reducing the number of B cells and T cells, alemtuzumab effectively “resets” the immune system. This can be beneficial in autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS), where an overactive immune response is causing damage to the body’s own tissues. Alemtuzumab’s effects on the immune system also make it useful in preventing organ rejection in transplant patients and treating certain types of leukemia. Alemtuzumab is a potent immunosuppressant, which means it can increase the risk of infections and other side effects. It is typically used in carefully monitored clinical settings with close patient monitoring.
References
Wikimedia Foundation. (2023, August 13). Alemtuzumab. Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alemtuzumab#:~:text=Alemtuzumab%20is%20used%20for%20the,%2Dmediated%20cytotoxicity%20(ADCC).
Leave a Reply