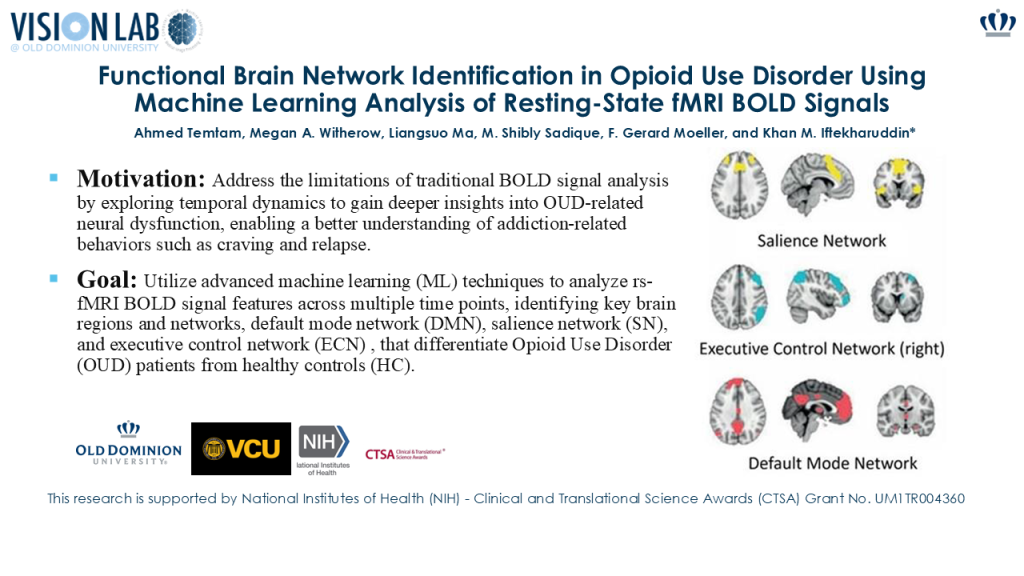
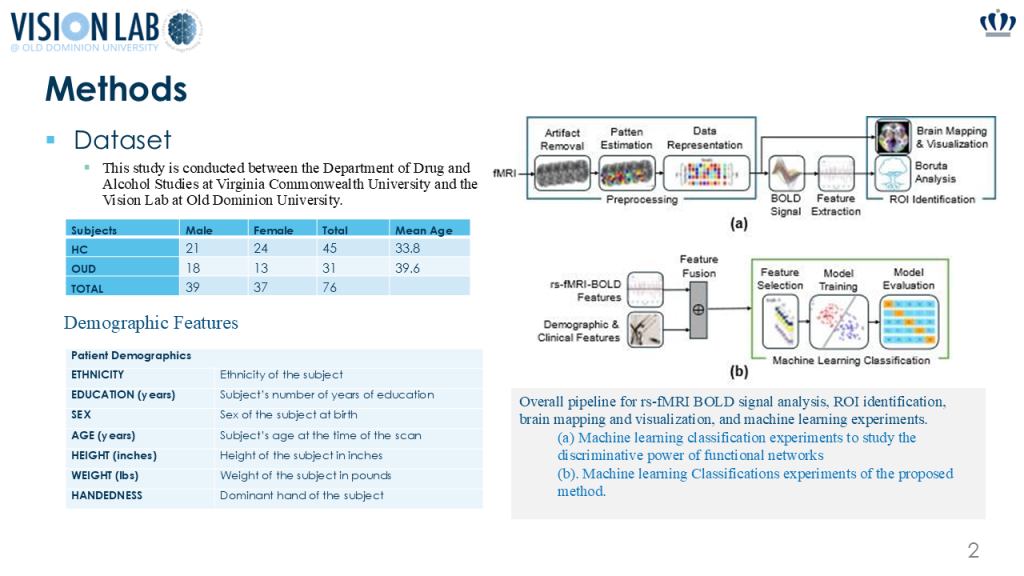
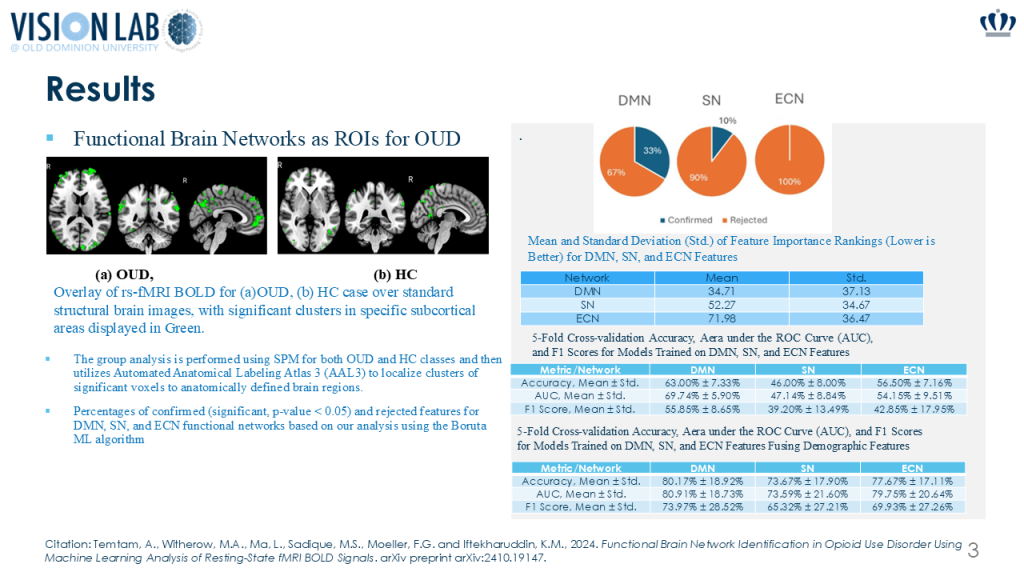
Understanding the neurobiology of opioid use disorder (OUD) using resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (rs-fMRI) may help inform treatment strategies to improve patient outcomes. This study uses machine learning (ML) and resting-state fMRI to analyze brain activity in three key networks: the Default Mode Network (DMN), Salience Network (SN), and Executive Control Network (ECN). The study applies three methods: (1) the Boruta ML algorithm to identify significant BOLD features distinguishing OUD from healthy controls (HC), (2) Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) with the AAL3 atlas to identify affected brain regions, and (3) ML classification. Findings highlight the DMN as the most discriminative network. These results may help improve diagnosis and treatment strategies for Opioid Use Disorder, ultimately leading to better outcomes for patients.